Back in 2010, Australia saw a surge in solar battery installations all around the country. Since then, about 3 million homes have enjoyed the perks of rooftop solar, including lower electricity bills than those with just a grid connection.
To paint a clearer picture, it is estimated that in NSW, per kilowatt of energy generated by solar panels saves you about $400 annually. You have a standard 6.6kW solar system on your rooftop, and your savings for the said year will be about $2640, which is $660 in a quarter!
There is a way in which you could get even more out of your solar panel system; what might that be? Adding a solar battery system is the answer.
However, batteries for solar systems are by no means a small investment, so the question remains: are solar batteries worth it in 2024 as a homeowner? We will find out soon enough. But first, let’s get to know some basics about solar batteries.
Types of Solar Batteries
Solar batteries, also called solar energy storage systems, play a crucial role in solar power setups by storing surplus energy generated during sunny periods for later use, such as during nights or overcast days.
These batteries come in various types, each with distinct characteristics and advantages.
Lead-acid batteries, including Flooded Lead-Acid (FLA) and Valve-Regulated Lead-Acid (VRLA) options, offer durability and cost-effectiveness, with VRLA batteries like Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) and Gel batteries being maintenance-free.
Lithium-ion batteries, such as Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4), Lithium Nickel Cobalt Manganese Oxide (NMC), and Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminium Oxide (NCA), provide high energy density, extended lifespan, and enhanced safety.
Flow Batteries, represented by Vanadium Flow Batteries, offer a liquid electrolyte and are known for their extended cycle life and scalable capacity.
Saltwater Batteries, specifically Sodium-Ion Batteries, are environmentally friendly and potentially cost-effective. Nickel-iron or Edison batteries are durable but have lower energy density. Hybrid Batteries combine different technologies for optimised performance.
Choosing the correct solar battery involves cost, space, maintenance, and intended application, while ongoing advancements in battery technology may introduce newer options.
Reasons Why You Should Get Solar Batteries
Solar battery prices are not low, but the payback period goes down with the price hike of energy in Australia every day, and due to the current economic environment, I can only see energy prices rise.
According to the Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO), the wholesale cost of power in the National Electricity Market (NEM) jumped by 141 per cent in the first three months of 2022 compared to the same quarter last year.
That said, storing the surplus of energy generated by your solar panels sounds like a sound investment, doesn’t it?
Here are some more reasons-
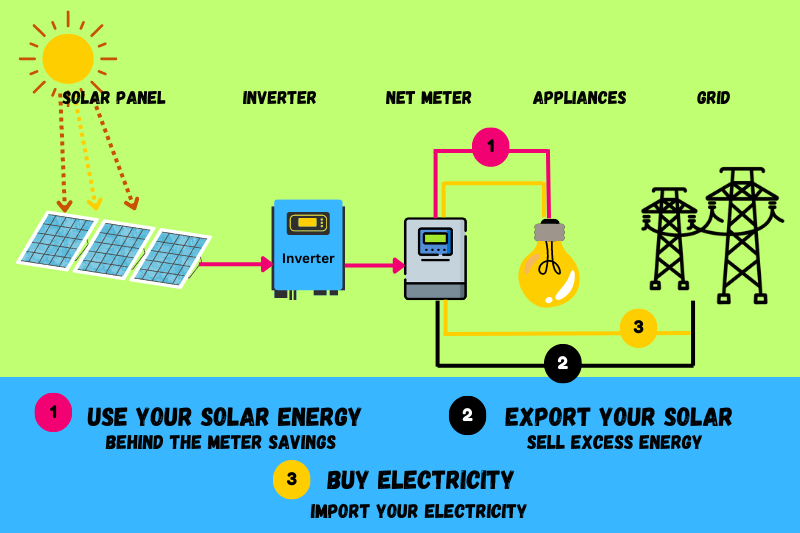
End of Net Metering in Australia
Net metering is a system that allows you to send the excess power generated by your solar panels to the grid and get a portion of the exact amount back on demand.
People were utilising the grid practically as a storage facility when the net metering system was still in place, but that luxury is no longer available.
Net metering was available until April 2020 in the Northern Territory; however, the benefit is no longer at one’s disposal for solar systems constructed after that date.
Essentially, with the end of net metering, you no longer have the freedom to get a one-to-one net metering service (a kW received per kW given).
That doesn’t mean you don’t have other means to store the energy in the grid; you do; however, that is not as beneficial as net metering and not certainly as profitable as having your solar battery.
Solar panels can generate a different amount of energy all day, as the sun doesn’t shine as bright from sunrise to sunset.
The maximum amount of electricity generated by the solar panels is between 12 and 3 pm. An average Australian household only consumes a little electricity during that time since they are the majority at work.
Studies have shown that, with the surge of electric prices off the grid, it needs to make more financial sense to store the excess energy in the grid; instead, having your solar battery and using it on demand will be much more profitable in 2023.
Electricity Prices are Higher at Night
As a storage unit does require significant investment, you decided to export the surplus of electricity to the grid.
But, keeping in mind that an average household requires more energy at night than in the day, you will be paying more to buy back that amount of electricity you exported at night.
So, it’s evident that storing the surplus in a solar battery makes more sense than repurchasing it at a higher electricity cost.
Grid Outages
There are occasions in which people suffer from grid outages. It can be during a scheduled check-up of the grid, a devastating storm, or just about any other reason. It’s more common than you would think. In those cases, a solar battery can be your resolve.
We are positive you would prefer to avoid coming home to a fridge full of rotten food. To have an uninterrupted supply of energy that you have all the control over, having a battery storage unit makes perfect sense.
Yes, of course, you could opt for a backup generator, but they are noisy, and it defeats the purpose of having installed solar on your rooftop in the first place. It runs on diesel, a non-renewable energy source contributing to carbon emissions.
Are Solar Batteries Worth It?

It makes sense for a large energy user to opt for solar batteries. They are worth the price, and here is why-
Solar battery cost is significantly coming down as we speak. For instance, back in 2020, a 6kw solar battery cost about $10,000, which now is about $7,700
It is the only way to go for those who live off the grid
Without the benefit of Fit, having one’s storage system saves on power bills even more
Complete control over your energy consumption
Power backup for days in the event of a power outage, and with the addition of solar panels, you can forget the grid.
Solar and Battery Package Price in Australia: How Much Do Solar Batteries Cost?
It’s tough to figure out the actual price of solar batteries because it depends on many variables. For example, it will depend on your power needs, whether you have any power-hungry appliances, household size, geographic location, etc.
Depending on these variables, you can determine how much of a storage unit you require. Thus, That’s how the cost of solar batteries is estimated.
But to give you a rough idea, the price of a kWh of residential solar battery storage can hover over the $1000 mark.
These include the cost of installation and GST. Remember that the battery brand and all the other factors mentioned matter in the end, and prices vary depending on those factors.
10kw Solar Battery Price
As of October 2023 in Sydney, NSW, the current cost of a 10kW solar battery paired with a 6.6kW solar panel system is $12,888. This price includes two 5.1 kWh modules integrated with a 6.6 kW solar system. The potential payback time for this system can be less than 4 years.
The Tesla Powerwall, which has a storage capacity of 13.5 kWh, costs approximately $1,150 per kilowatt-hour.
When considering the broader market, solar batteries without the solar component typically fall from $900 to $1,200 per kilowatt-hour. The specific pricing varies based on the brand and model.
6kw Solar Battery Cost

The solar battery storage cost is how much you pay for each unit of electricity it can store, and it’s usually measured in dollars per kilowatt hour ($/kWh).
Typically, these batteries cost between $900 and $2,000 per kilowatt-hour. If you want a solar setup with a 10.2-kilowatt-hour battery and a 6.64-kilowatt solar system, it might cost you around $12,888.
If you just want the battery alone, without the solar system, a solar battery alone can cost $990 per kilowatt-hour. It includes a particular device called a hybrid inverter that connects the battery to the solar system.
For a specific type of battery called the Tesla Powerwall, which has a 13.5 kilowatt-hour capacity and comes with its inverter, the price is $1200 per kilowatt-hour.
Another type of battery, the Sungrow 9.6 kilowatt-hour solar battery, is priced at $1227 per kilowatt-hour. This cost includes a 5-kilowatt hybrid inverter.
If you’re looking at a solar panel system with a 6-kilowatt capacity, and it includes a battery with a capacity of 16.6 kilowatt-hours, the total cost for installing this combined system can range from about $19,935 to an average of $25,235.
The exact price depends on the type and quality of your chosen system. For more details, check out how much a 6kW solar battery costs in Australia.
Solar battery ROI
The return on investment (ROI) for solar batteries in Australia is influenced by various factors, such as the system’s initial cost, local electricity rates, solar generation capacity, and available government incentives or rebates.
Key considerations include the upfront expenses encompassing the battery, inverters, installation, and related components.
The cost of grid electricity in your area is pivotal, with higher rates potentially leading to faster returns, as stored solar energy use during peak periods saves on electricity bills.
Solar panel efficiency, battery performance, and lifespan also impact long-term returns. Government incentives, rebates, and electricity consumption patterns, especially during high-demand periods, contribute to overall ROI.
Monitoring technological advancements is crucial for assessing the economic viability of solar battery systems over time.
Seeking professional analysis and staying informed about industry trends and policy changes are advisable for making well-informed investment decisions in Australia.
How To Choose Solar Batteries?

To choose solar batteries in Australia, consider your energy needs, capacity and performance, compatibility with your solar system, warranty, and cost. Assess the battery’s kilowatt-hours (kWh) storage capacity to match your daily usage.
Look for reliable brands and models with proven performance and longer lifespans. Ensure compatibility with your existing solar system, and check for government incentives or rebates. Compare the cost per kilowatt-hour and warranty terms.
Consider factors like installation requirements and whether the battery supports backup power. Seek professional advice to tailor your choice to specific needs and conditions.
State Rebates for Solar Batteries
State rebates for solar batteries vary across Australia. States like South Australia, Victoria, and Queensland offer specific incentives and rebates for solar batteries.
However, rebate programs and amounts can change, so it’s crucial to check the latest information from your state government or relevant authorities for the most up-to-date details on solar battery rebates.
Solar Battery FAQs
What Size Solar Battery Do I Need to Power a House?
The size of the solar battery needed to power a house in Australia depends on various factors, including your energy consumption, the size of your solar panel system, and your specific energy needs.
On average, a medium-sized household might require a solar battery with a capacity ranging from 5 kWh to 20 kWh.
To determine the appropriate size, consider your daily electricity usage, the sunlight your location receives, and whether you want the battery to provide backup power during outages.
It’s advisable to consult with a solar energy professional to assess your specific requirements and design a system that meets your energy goals.
Is a Solar Battery Worth it?
Deciding whether to invest in home battery storage depends on various factors. Your energy consumption, goals, and dependence on the grid play crucial roles.
A battery could be valuable if you experience frequent power outages or seek backup power. Explore your area’s government incentives, rebates, and electricity rates to assess the financial benefits.
A good solar panel system may increase the potential advantages of integrating a battery. Consider the environmental impact, battery lifespan, and technological trends. To make an informed decision, consult with solar professionals like Solar Emporium.
We can tailor advice to your specific needs and circumstances, keeping in mind that the evolving landscape of technology and market conditions may influence the long-term value of a solar battery investment.
If you want to sit down with one of our solar experts and see if solar batteries make sense, contact us today! Reaching out for help is okay; we are here to serve YOU.