Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are always available and can be used again and again, like the sun, wind, water, and trees. Australia has an abundance of these natural sources. And many companies and homes are choosing to invest in renewable energy.
Using renewable energy can save a lot of money compared to using energy from the grid. It helps businesses lower their emissions, improve their sustainability, and avoid future price increases.
It means that renewable energy for the future economies of Australia has huge potential for growth. And it will create many opportunities from various sources of renewable energy.
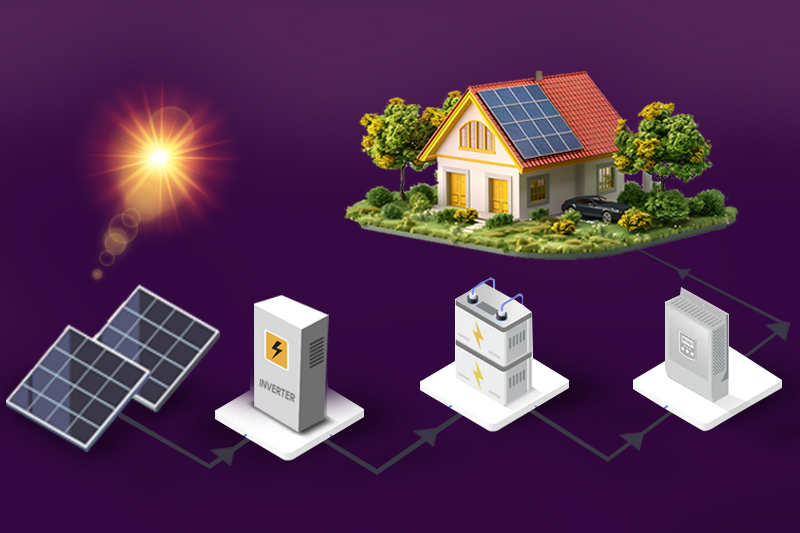
The most common renewable energy option for Australian businesses is generating energy on-site. Solar panels, wind energy, and biomass/biogas are widely used.
When reducing carbon emissions is the main goal, many businesses also buy some renewable energy from an energy retailer.
The costs and benefits of investing in renewable energy can be very different for each situation. To get the best energy and financial results, it’s important to get advice from an independent expert or certified system designer.
Various Renewable Energy Sources for the Future Economics of Australia
Solar Panels
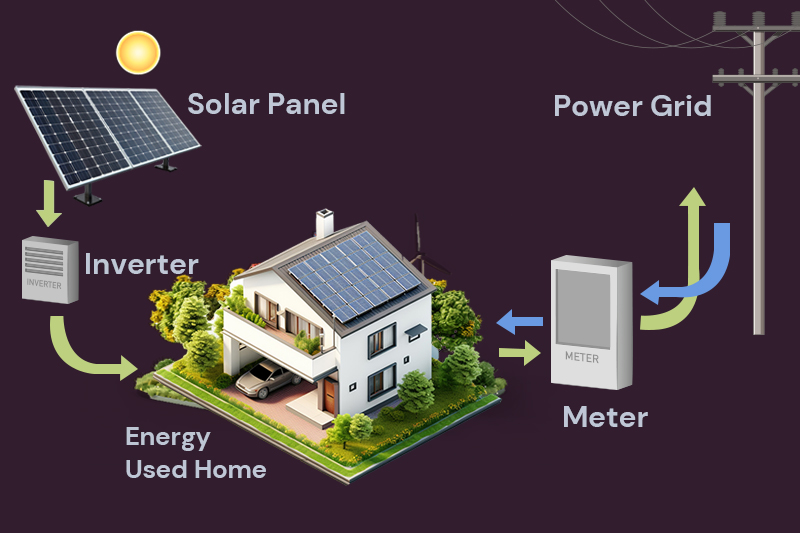
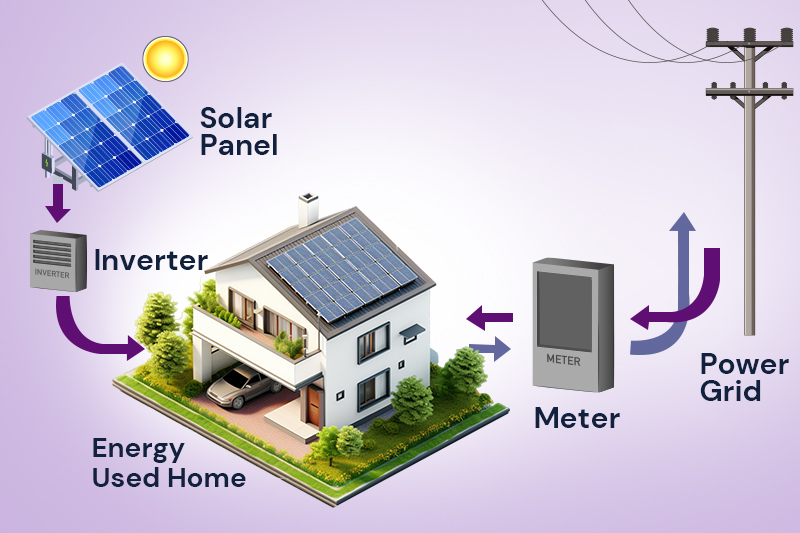
When sunlight hits a solar panel, it turns the light into electricity that can be used on-site or sent to the grid. Solar power is now the cheapest way to get electricity, and Australia is a world leader in rooftop solar.
By the end of October 2023, over 3.5 million homes in Australia had solar panels, meaning more than one in three houses had them.
The Australian Government has a new Solar Consumer Guide that gives free expert advice on using rooftop solar and batteries for businesses.
The guide helps you choose, use, and maintain a solar system that fits your needs and saves you money. It also tells you about ways to reduce costs.
Battery Storage
Renewable energy can be stored in batteries, offering many benefits for businesses. Solar battery storage allows you to use more on-site renewable energy instead of buying grid electricity.
It also lets you store grid electricity when it’s cheap and use it later. If set up correctly, batteries can provide backup power during short outages.
Lithium-ion batteries are common and used in everything from phones to large-scale batteries.
Researchers and industry are exploring new technologies to complement lithium-ion batteries, such as different battery types and other energy storage methods, such as thermal and mechanical storage.
Wind
Wind power uses turbines to turn wind energy into electricity. Wind energy produces over 30% of Australia’s renewable energy and is the cheapest source of large-scale renewable energy.
New designs have made wind power more efficient with larger, lighter blades and smarter turbines that collect real-time data.
Wind power is a major part of the national grid but is not as cost-effective as solar for on-site generation. Large companies often buy off-site wind energy for a consistent and cheap renewable energy source.
Bioenergy
Bioenergy is made by burning or breaking down biological matter. Biomass can be burned or turned into natural gas, while biogas (methane and CO2) can produce electricity and heat.
Bioenergy is proven to reduce waste and carbon emissions, and it is especially useful for industries like food, pulp and paper, and dairy manufacturing. Biomass can also make biofuels like ethanol, low-carbon diesel, and aviation fuels.
Hydropower
Hydropower uses moving water to generate electricity and is a mature technology. In 2018, it provided about 7.5% of Australia’s electricity.
It typically uses dams on rivers, capturing energy as water flows through turbines. Smaller systems in rivers can expand hydropower production.
Hydropower can also store energy by moving water uphill for later use, like in the Snowy 2.0 project.

Geothermal
Geothermal energy uses heat from the earth. Pumps or poles transfer this heat for heating, cooling, and other uses. It works well in places with balanced heating and cooling needs, like schools, hospitals, and hotels.
However, due to excavation and infrastructure costs, it could be more cost-effective for most applications and is best used in new buildings.
Geothermal heat pumps are especially helpful when it gets too cold for air-to-air heat pumps. Some industrial businesses with lots of excess heat benefit very little from geothermal, but it can be useful in underground mines with easy access to geothermal resources.
Renewable Energy's Role in the Future Economies of Australia
Economic Benefits
- Job Creation: Renewable energy projects create many jobs. For example, people are needed to install and maintain solar panels and wind turbines. This helps reduce unemployment and boosts the economy.
- Cost Savings: Over time, renewable energy can be cheaper than fossil fuels. Solar and wind energy, once set up, have very low running costs. This means that both people and businesses can save money on their energy bills.
- Attracting Investment: Renewable energy is the future, so it attracts investors. When companies invest in Australia’s renewable energy projects, more money enters the country, helping the economy grow.
Environmental Benefits
- Reducing Pollution: Renewable energy produces much less pollution than fossil fuels. This means cleaner air and water, which is better for everyone’s health.
- Combating Climate Change: Using renewable energy helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions, which are a major cause of climate change. This helps protect Australia’s environment for future generations.
Energy Independence
- Less Reliance on Imports: By producing renewable energy, Australia doesn’t have to buy as much energy from other countries, making it more independent and secure.
- Stable Energy Prices: Renewable energy sources are not subject to the same price fluctuations as fossil fuels. This means more stable and predictable energy prices for consumers and businesses.
Technological Advancement
- Innovation and Research: Investing in renewable energy promotes innovation. New technologies are developed to make renewable energy more efficient and cheaper, creating new industries and opportunities for growth.
- Global Leadership: By leading in renewable energy, Australia can set an example for other countries. This can enhance Australia’s reputation on the world stage and lead to new international partnerships and trade opportunities.
Sustainable Development
- Long-term Growth: Renewable energy provides a sustainable way to power the economy. Unlike fossil fuels, which will eventually run out, renewable energy can be used indefinitely, ensuring long-term economic stability.
- Protecting Natural Resources: Using renewable energy helps conserve Australia’s natural resources, ensuring they are available for future generations.
Renewable energy is essential for the future of Australia’s economy. It creates jobs, saves money, attracts investment, and protects the environment.
By investing in renewable energy, Australia can enjoy a stronger, more sustainable, and more independent economy. This will benefit the country today and secure a better future for future generations.
Jobs in Renewable Energy

The renewable energy sector includes many jobs, such as:
Solar Panel Installers: They set up solar panels on rooftops or other structures.
Wind Turbine Technicians: They maintain and repair wind turbines.
Environmental Engineers: They design renewable energy projects.
Project Managers: They oversee renewable energy projects to ensure they are completed on time and within budget.
Future Growth in Australia
Australia is focusing more on renewable energy, leading to a big increase in related jobs. Here’s why:
Government Support: The Australian government is investing in renewable energy projects.
Technological Advances: New technology is making renewable energy more efficient and cheaper.
Climate Goals: Australia has set goals to reduce carbon emissions, increasing the need for renewable energy.
Financing Renewables
Buying renewable energy systems can save a lot of money, but the initial cost and other investment barriers can make it hard for some to take action.
Fortunately, there are financing options to help everyone overcome these barriers and benefit from renewable energy.
The Clean Energy Finance Corporation (CEFC) collaborates with banks and other financiers to provide attractive financing options at better rates than usual. Many companies also offer financing plans for businesses that want to install solar panels.
If a business does not own the building or land, it might be possible to make a deal with the building owners to add renewable energy systems as part of the lease. The Australian Government offers resources on green leases to help with this.
Australia is ready to become a global leader in renewable energy, harnessing its abundant natural resources, such as sunlight, wind, water, and biomass.
This shift to renewable energy promises substantial environmental benefits, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions and pollution, and also offers significant economic advantages.
The transition is creating new jobs, reducing energy costs, and attracting substantial investments, all of which contribute to a more sustainable and robust economy.
Innovations in solar panel systems, wind energy, bioenergy, hydropower, and geothermal energy are paving the way for a greener future.
Solar energy, particularly, has become the cheapest source of electricity, with Australia leading the world in rooftop solar installations.
In conclusion, Australia’s commitment to renewable energy is not only addressing environmental challenges but also fostering economic growth and stability.
Solar Emporium is here to support your renewable journey! Contact us today or get a free solar quote!