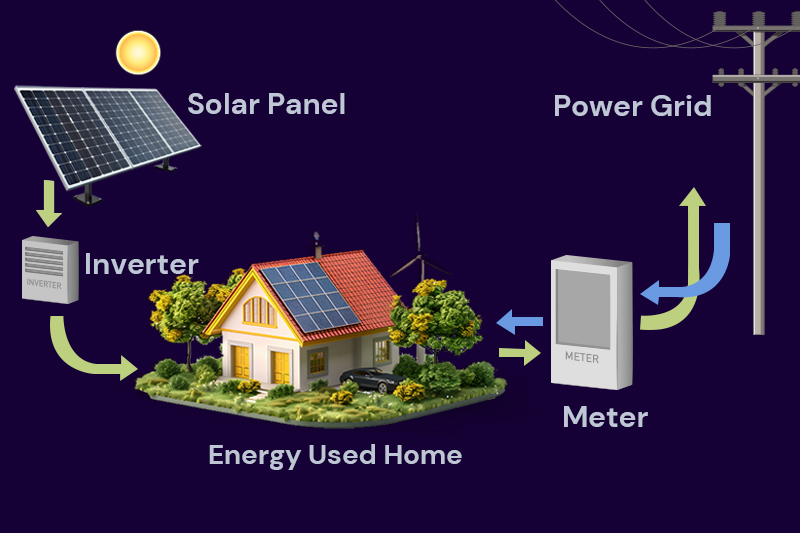
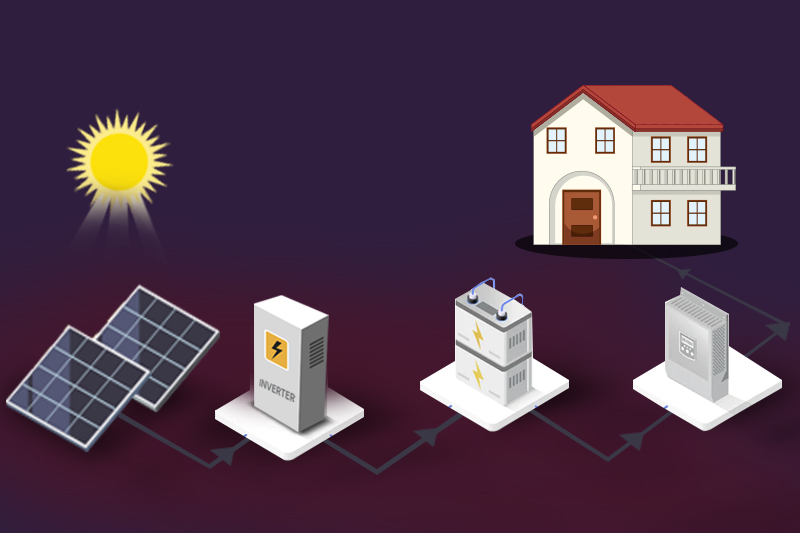
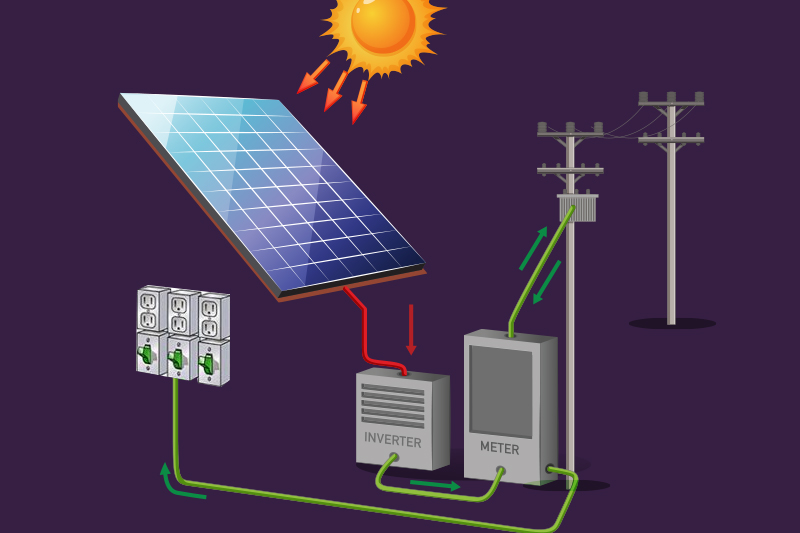
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has greatly changed the solar energy industry recently. AI is improving solar energy production, monitoring, and management, which helps save money and improve efficiency.
This technology is helping solar energy reach new levels, benefiting businesses, the environment, and the future of energy.
But how exactly is AI revolutionizing solar energy in Australia? And what role will machine learning, a part of AI, play in helping Australia move to a zero-carbon energy future?
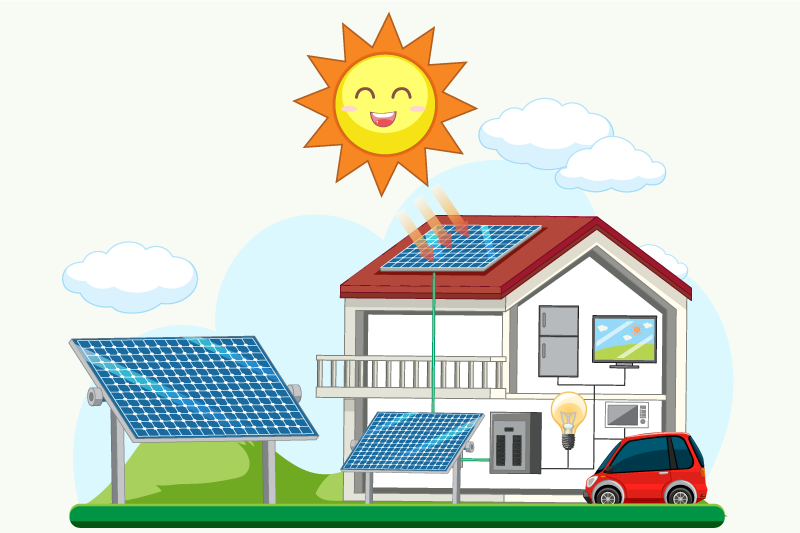
Solar energy has been available for many years, but its use has been limited due to high costs, low efficiency, and the fact that sunlight isn’t always available.
Recent technological advances have made solar energy cheaper and more efficient, making it a better option for homes and businesses.
Government incentives and subsidies have made solar energy more appealing to people who want to reduce their carbon footprint and save on energy bills.
AI helps solve problems in the solar industry, such as accurately predicting energy needs, improving energy storage, and lowering maintenance costs.
The Promising Future of Artificial Intelligence
AI has a bright future ahead. Businesses, governments, and people are quickly adopting AI as it continues to improve.
AI can change many parts of our daily lives, from healthcare to transportation and communication. AI can help us focus on what truly matters by making our routines easier.
Artificial Intelligence is used in many ways, such as helping doctors diagnose diseases and enabling robots to assist in surgeries.
As AI technology advances, it will become even more widespread and sophisticated. The future of AI is promising and has the potential to revolutionize our lives.
Applying AI to Renewable Energy Technologies
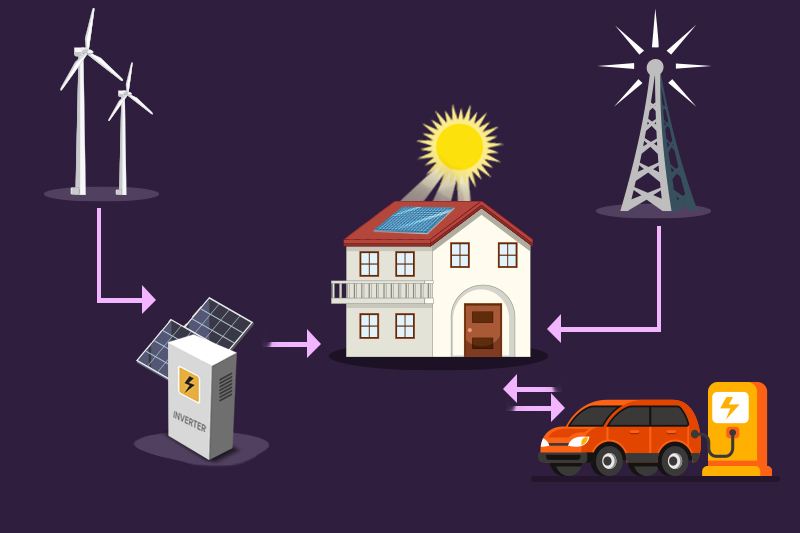
In the next 10–15 years, more renewable energy sources like wind and solar will be used, while older power sources like coal will be phased out.
This will require careful balancing to match energy supply with demand and prevent grid failures. Machine learning can help with this.
Machine learning uses algorithms to analyze large amounts of data to find trends and patterns. These algorithms make predictions based on programmed rules and the data they receive. They learn and improve over time by identifying patterns and adjusting their rules.
Machine learning is also based on climate science to improve models and track climate change effects.
In the electricity sector, machine learning can enhance how energy is distributed and used in the grid. As more renewable energy sources are added, utilities need better ways to predict energy needs in real-time and in the future.
Existing algorithms can forecast energy demand, but they could be improved by considering detailed local weather, climate patterns, and household behavior.
The Need for AI in Energy and Utilities

Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming more important in the energy and utility sectors. AI helps meet growing demands and reduces the environmental impact of energy generation, storage, and distribution. It enables automation, pattern recognition, data analysis, and predicting energy needs.
AI can also spot and predict problems with energy infrastructure and offer smart solutions, making energy systems more efficient, reliable, and cost-effective.
AI can analyze past data, weather patterns, and other information to forecast energy demand accurately. This helps energy providers plan better, reduce waste, and lower costs. With this predictive analysis, energy providers manage resources more efficiently, leading to a sustainable energy future.
Using advanced AI technology, energy providers can better predict usage, reduce waste, and improve efficiency. This results in a more reliable, affordable, and sustainable energy system.
As technology progresses, the energy and utilities industry has a bright future. We can create a more sustainable world for future generations using the latest innovations.
The endless opportunities, from renewable energy sources to advanced solar storage solutions, make a greener future possible.
Artificial Intelligence Applications in the Energy Sector
Energy Demand Forecasting:
Optimizing Energy Production:
Optimizing Energy Storage:
Asset Maintenance:
Grid Management:
Solar-Powered Transportation:
Reducing Carbon Footprint:
Energy Use Efficiency:
AI can revolutionize how we use and manage energy by identifying inefficiencies and sources of waste. It can detect energy theft and other issues, increasing energy sustainability and efficiency.
Overall, AI has the potential to transform the energy sector, making it more efficient, reliable, and sustainable.
Artificial Intelligence Methods for Solar Energy

A recent survey found that over 90% of renewable energy workers use digital tools and automation to exploit their advantages.
With proper guidance, these professionals leverage automation and digitalization to stay competitive in the current energy landscape. By embracing the latest digital technologies, they open up endless possibilities.
Artificial intelligence (AI) can be used in the energy sector in two main ways: automated and aided decision-making. Automated decision-making means AI systems make decisions on their own without human help.
On the other hand, aided decision-making involves AI assisting humans by providing insights and recommendations. Both methods can enhance energy production and consumption by increasing efficiency and effectiveness.
Automated decision-making uses AI to analyze large amounts of data and make decisions based on that analysis. For example, AI can adjust a building’s temperature by considering occupancy patterns, weather conditions, and energy use data.
An AI system can look at data from various sensors, such as temperature, motion, and light, to set the best temperature for different building parts. This optimization can save energy and reduce carbon emissions by lowering energy consumption and HVAC costs.
Aided decision-making uses AI to help humans make better decisions. By analyzing data, AI can find areas that need improvement and suggest ways to optimize processes.
For example, an AI system can examine energy usage data to identify locations that benefit from better energy efficiency. The system can then provide recommendations on maximizing energy efficiency in those areas, helping decision-makers make better business choices.
Both approaches are powerful tools for improving energy production and consumption efficiency and effectiveness.
Automated decision-making reduces the need for human involvement and increases efficiency, while aided decision-making helps humans make better-informed decisions based on data-driven insights and suggestions.
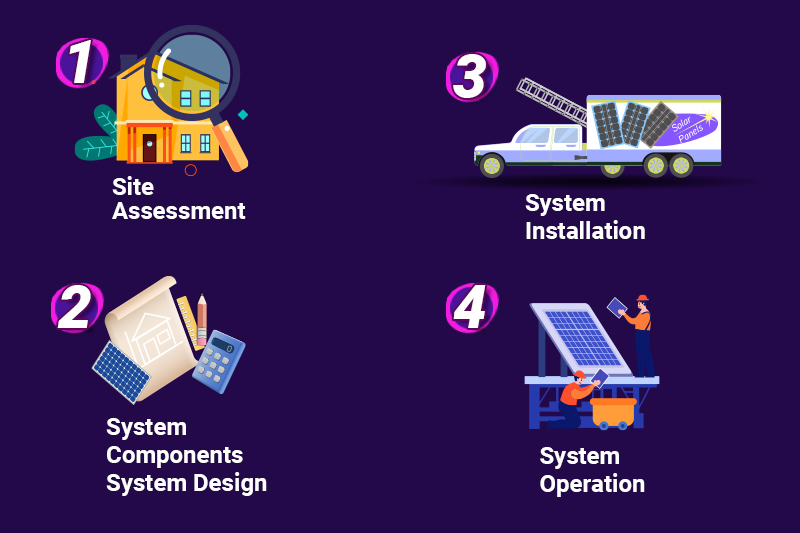
Machine Learning Algorithms for Solar Installation

Using machine learning algorithms for solar installation is a new technology that is changing how we use and manage solar energy.
These algorithms help identify the best conditions for installing solar panels, such as the ideal roof tilt, orientation, and placement. They allow solar installers to optimize performance and cost.
Choosing the Best Location:
Machine learning algorithms analyze weather patterns, sunlight levels, and the landscape to find the most efficient and cost-effective spots for solar panels.
Using advanced AI, they compare many factors to decide the best setup for each installation, ensuring maximum energy production.
Design Optimization:
Performance Prediction:
Machine learning is also used to predict how well solar panels will perform. These algorithms can spot potential issues by analyzing sunlight levels and weather data and suggest the best maintenance schedules.
It ensures solar panels work efficiently and helps make better decisions about maintenance and new installations.
Using machine learning algorithms can greatly improve the performance and efficiency of solar panel installations.
We are experiencing systemic change in the energy industry and have the opportunity to lay the groundwork for a clean energy future.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the solar energy industry. The combination of AI and solar power transforms the industry and demonstrates what a renewable and sustainable future can look like.
If you want to be part of this revolution of the solar energy industry, please contact Solar Emporium.