The residential solar industry in Australia is large and growing. With over three million solar panel systems now installed in Australian homes, you might believe that solar installation is a routine and quality-assured job.
However, regulatory bodies receive hundreds of yearly complaints about faulty or underperforming installations.
The popularity of solar panels has increased complaints about solar companies. The Clean Energy Regulator has also conducted inspections of residential solar installations, which revealed that many installations need to be performed or correctly configured.
So how do you ensure a proper residential solar panel installation? The installation process for a solar panel system in Australia involves several steps to guarantee an appropriate setup and compliance with regulations.
Process Of Residential Solar Panel Installation
Assessment and Planning
Determine your energy needs: Understand your household’s electricity consumption patterns to determine your required solar system size.
Roof assessment: Evaluate the suitability of your roof for solar panels. Factors such as roof orientation, shading, and structural integrity are considered.
Obtain quotes: Get multiple quotes from solar installation companies. These quotes should include the system size, panel types, inverter technology, warranties, and estimated costs.
Choose a Solar Installer
- Research and select a reputable solar installer. Look for companies with experience, positive reviews, and proper licensing.
- Check if they are accredited: The Clean Energy Council (CEC) provides accreditation to solar installers in Australia. Choosing an accredited installer ensures compliance with industry standards.
System Design
Permits and Approvals
Book Your Equipment
Installation
Inverter Installation
Electrical Work
Testing
Grid Connection
Paperwork and Documentation
Final Inspection and Approval
Sometimes, local authorities or your network distributor may perform a final inspection to ensure the system meets safety and compliance standards.
It’s important to note that specific details of the installation process can vary based on the location, installer, and regulatory requirements in different parts of Australia.
Working with a qualified and accredited solar installer is essential to ensure a smooth and compliant installation process for your solar panel system.
What’s An Ideal Solar Installation Company?
Check Accreditation
Research Reputation
Experience Matters
Multiple Quotes
Quality Products
Warranties and Guarantees
Site Assessment
Transparency
Insurance Coverage
Ask for References
Check Licences
Verify that the installer holds the licences and certifications required by local authorities and regulatory bodies.
Remember that investing in a quality installation with a reliable installer can save you money in the long run and ensure the longevity of your solar system’s performance. Take your time to research and choose an installer that aligns with your needs and priorities.
Components Of Solar Panel System

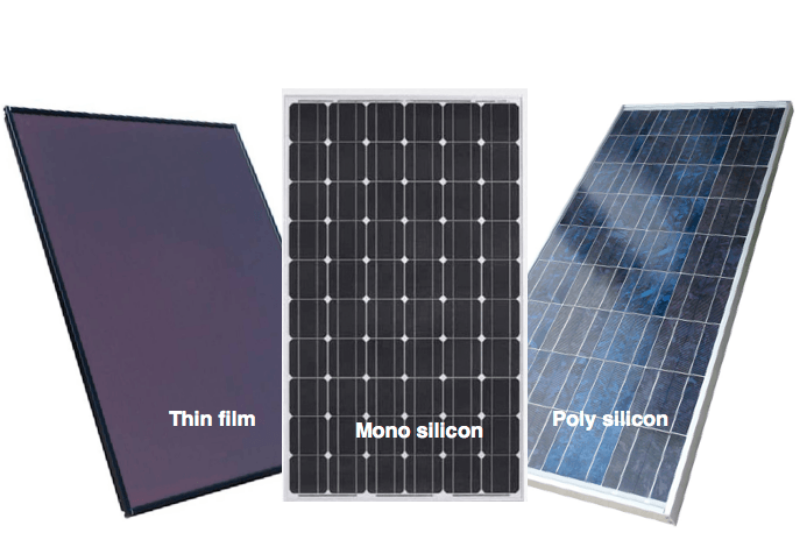
- Solar Panels (Photovoltaic Modules)
- Inverter
- Mounting System
- Racking and Frames
- Wiring and Cables
- DC Disconnect Switch
- AC Disconnect Switch
- Monitoring System
- Net Meter
- Solar Battery/Battery Storage (Optional)
- Grounding Equipment
Why Solar Emporium As Your Desired Solar Installer?

Choosing Solar Emporium as your solar panel, installer has many compelling benefits that make them an outstanding choice for your renewable energy journey.
Proven Expertise: With a wealth of experience in the solar industry, Solar Emporium stands as a trusted name in the field. Our team of skilled professionals brings a deep understanding of solar technology and installation practices, ensuring a seamless and efficient process.
Clean Energy Council Accreditation: Solar Emporium proudly holds Clean Energy Council (CEC) accreditation, a testament to its commitment to adhering to industry best practices and delivering top-quality installations. This certification underlines the dedication to excellence and compliance with the highest standards.
Tailored Solutions: Recognising that every home is unique, Solar Emporium specialises in crafting customised solar solutions that perfectly align with your energy needs, budget, and aesthetic preferences. We work closely with you to design a system that maximises energy production and fits seamlessly into your property.
High-Quality Components: Solar Emporium’s dedication to excellence extends to its components. We prioritise sourcing high-quality solar panels, inverters, and other equipment from reputable manufacturers.
This focus on premium materials ensures your system’s reliability and long-term performance.
Exceptional Customer Service: Exceptional Customer Service: Customer satisfaction is at the heart of Solar Emporium’s ethos. Our team is dedicated to giving you a great customer experience, from when you show interest in the installation to afterward. They’re readily available to address your queries and concerns.
Transparent Process: Solar Emporium believes in transparency every step of the way. We take the time to explain the installation process, pricing details, and any available incentives or rebates. This open approach empowers you to make well-informed decisions with confidence.
Efficient Installation: The skilled installers at Solar Emporium are experts at executing installations efficiently without compromising quality.
Warranties and Support: Solar Emporium takes pride in the durability and reliability of its installations. This commitment to customer satisfaction extends beyond installation day.
Positive Impact: By choosing Solar Emporium, you’re contributing to a cleaner environment and reducing your carbon footprint. Solar energy helps decrease reliance on fossil fuels and promotes a more sustainable future for future generations.
Local Focus: As a local business, Solar Emporium understands the unique energy landscape of the region. Our insights into local regulations, grid connections, and available incentives ensure a smooth installation process tailored to your location.
With our expertise, commitment to quality and customer-focused approach, we are determined to guide you towards harnessing the sun’s power and enjoying the benefits of a well-designed solar panel system.
Solar Emporium shines as a partner you can trust in the journey towards cleaner and more affordable energy. Get a free solar quote today!