Using new and growing renewable energy sources is essential for keeping our energy use sustainable and protecting the planet from climate change.
Biogas and solar energy, both renewable and environmentally beneficial, are the focus of our comparison today. Their potential to transform Australia’s energy landscape is a source of inspiration and hope for a sustainable future.
Biomass is renewable because we can plant new crops after each harvest, and it produces low carbon emissions. Using renewable energy helps reduce our carbon footprint and protect the environment.
Exploring renewable options is essential as we look for cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. Biomass and solar energy are great alternatives to fossil fuels, each with benefits.
Biomass uses organic materials like wood, crop leftovers, and waste to create heat and electricity. Solar panels turn sunlight into clean electricity.
Understanding the differences between these renewable energy sources helps us make better choices for our future energy needs.
Let’s explore the advantages, disadvantages, and comparison of biomass and solar energy and how they can help create a more sustainable future.
Understanding Biogas
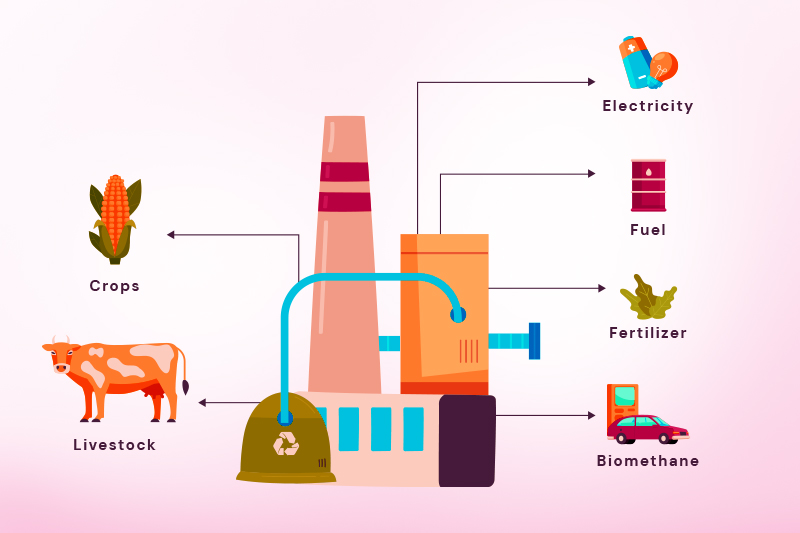
Biogas is produced when biomass decomposes naturally or in an industrial anaerobic digester. Another way to consider the differences is that biomass is the raw material, whereas biogas is the finished product.
Biomass energy creates heat or electricity using organic materials like wood, crop leftovers, and waste. This renewable energy source has been used for many years and is a reliable solution.
How Biomass Energy Works
Biomass energy systems use the energy stored in organic materials. These systems convert wood, crop leftovers, and waste into heat and power through various processes.
Biomass Combustion for Heat and Power
The primary process in biomass energy is burning organic materials in special furnaces or boilers to produce heat. This heat can be used directly to heat buildings or create steam that drives turbines to generate electricity.
Biomass combustion can be used in many settings, from home heating to large power plants, providing reliable and renewable energy.
Biomass Conversion into Biofuels
Biomass can also turn into liquid biofuels like ethanol and biodiesel. These biofuels are cleaner and more sustainable than fossil fuels.
Ethanol ferments sugars or starches from plants like corn or sugarcane, while biodiesel is made from vegetable oils or animal fats. These biofuels can be mixed with traditional fuels or used in vehicles, reducing our reliance on petroleum.
Advantages and Challenges of Biomass Energy Systems
Biomass energy systems have many benefits, like generating renewable energy and reducing waste. However, they also have challenges, such as air pollution from burning biomass and competition with food production. Sustainable practices and careful planning are needed to address these issues and make biomass energy a valuable part of our renewable energy mix.
Benefits of Biomass Energy
Biomass energy is versatile and widely available. It creates jobs in forestry, agriculture, and waste management and helps reduce landfill waste and pollution by using organic materials for energy.
Challenges and Limitations of Biomass Energy
The challenges of biomass energy include environmental impacts from harvesting and burning biomass, which can lead to habitat loss and air pollution. There is also competition between using land for biomass and food production, which can affect food security.
Sustainable land management and resource planning are essential to overcome these challenges and ensure biomass energy remains a viable renewable energy source.
Solar Panels

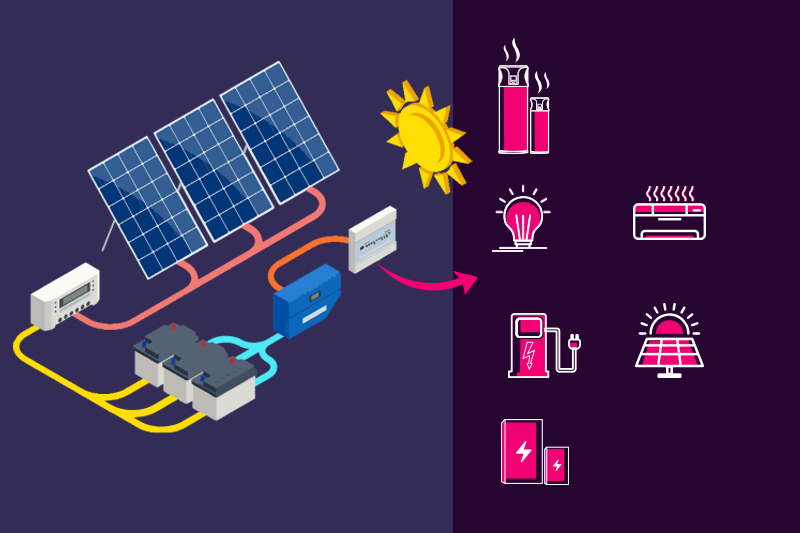
Solar panel, also known as solar panel system or photovoltaic (PV) system, convert sunlight into electricity using unique materials called semiconductors. Sunlight excites electrons inside the solar panel’s cells, creating an electric current.
This current is direct current (DC) electricity. Since most homes and businesses use alternating current (AC) electricity, an inverter is used to change DC into AC, making it usable for everyday electrical needs.
Advantages of Solar Panels
Clean and Renewable: Solar energy doesn’t produce greenhouse gases or air pollution, making it environmentally friendly and sustainable.
Low Operating Costs: Solar panels are cheap to run once installed since they only require sunlight. They require little maintenance, saving money over time.
With their adaptability and Scalability, solar panels can be tailored to meet a variety of energy needs, from small residential setups to large commercial projects. Their versatility offers a promising outlook for the widespread adoption of renewable energy.
Limitations and Challenges of Solar Panels
Dependence on Sunlight and Weather: Solar panels need direct sunlight to work well. Their efficiency drops with cloud cover, shade, and at night. Alternative energy sources or storage solutions are necessary when the sun isn’t shining.
High Initial Costs: Although prices for solar panels have dropped, the initial cost of buying and installing them can still be high. Despite the long-term savings, this upfront expense can be a barrier for some people.
Solar panels, a promising and popular renewable energy option, offer a clean and sustainable electricity solution with minimal environmental impact.
Despite some challenges, technological advancements and supportive policies are paving the way for solar power to play a significant role in our more sustainable energy future.
Comparing Biomass and Solar Panels
Biomass: While renewable, biomass energy can have environmental issues if not managed well. Harvesting biomass like wood or crop leftovers can lead to deforestation and habitat loss if done carelessly.
Burning biomass can also release pollutants into the air, causing air pollution and health problems for nearby communities.
Solar Panels: Solar panels provide a much cleaner way to generate electricity. They use sunlight to produce electricity without releasing greenhouse gases or other pollutants. This makes solar energy an eco-friendly option that helps fight climate change and reduce air pollution.
Cost Considerations
Biomass: Biomass energy systems can have lower fuel costs, but the initial setup can be expensive. Infrastructure, equipment, and transportation costs can be high, making it less practical for smaller projects.
Solar Panels: Solar panels also have high upfront costs for purchase and installation. However, these costs are balanced by long-term savings on energy bills. Additionally, there are often incentives like tax credits or rebates from government or utility programs that can help reduce the overall cost over time.
Energy Efficiency
Biomass: The efficiency of biomass systems can vary. Traditional methods may be less efficient than advanced techniques, such as gasification or pyrolysis, which can minimize energy losses during processing and combustion.
Solar Panels: Solar panels are generally very efficient, converting sunlight directly into electricity. While efficiency can vary based on factors like sunlight intensity and panel quality, improvements in solar technology have made them a reliable and efficient choice.
Suitability for Different Locations
Biomass: Biomass energy systems need access to biomass feedstock, which refers to the organic materials used as fuel, such as wood or crop leftovers.
This feedstock might only be available in some areas. Transporting and storing biomass can be challenging, especially in remote or rural locations.
Solar Panels: Solar panels can be installed almost anywhere with enough sunlight, making them a flexible option. They can be placed on rooftops, on the ground, or even on building facades, providing clean energy in various settings, from cities to rural areas.
Both biomass and solar panels have benefits and challenges. Biomass can provide reliable energy and use organic waste but can also have significant environmental impacts and cost issues.
Solar panels offer clean, efficient power with minimal environmental impact and can be used in many locations. Considering these factors, people can choose which renewable energy source.
Australia’s Move Towards Biogas
Australia is making significant progress in biogas development as part of its renewable energy efforts. One critical project is the Malabar Biomethane Injection Project in New South Wales.
This project upgrades biogas from the Malabar wastewater treatment plant into biomethane, which is then added to the natural gas network. This shows that biogas can be technically and commercially successful in Australia.
This project, funded by the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA), highlights biogas as a flexible resource that can help balance the energy grid. It also emphasizes biogas’s environmental benefits, such as reducing landfill waste and greenhouse gas emissions.
In Australia, biogas is produced through anaerobic digestion, where bacteria break down organic material without oxygen, creating biogas.
This biogas can be used for electricity, heating, and vehicle fuel. This process also creates nutrient-rich fertilizer, supporting a circular economy.
Australia’s biogas sector is expected to grow in 2024, driven by more projects and a rising interest in sustainable energy. These efforts are part of a larger plan to diversify energy sources and reduce reliance on fossil fuels, which aligns with global sustainability goals.
Choosing the Right Renewable Energy Source
Biomass and solar panels are essential for reducing reliance on fossil fuels and moving towards a sustainable energy future. Selecting the best option involves considering location, resource availability, and specific energy needs.
For any solar energy needs, contact Solar Emporium and get a free solar quote today!