If you are looking forward to starting to live off the grid, sorting through different options for power generation is extremely important. There are many stand-alone systems that can generate energy for your household which are completely green, sustainable and carbon emission free. Although all these options may seem attractive, you are going to have to make the call to choose the one that is suitable for your house, keeping all the other aspects in mind.
The article is intended to help you through the process. On that note, here’s how to generate power off grid explained.
Different Renewable Energy Sources for Your Home
As we are mainly looking into powering a residential property or a small farm or business, this suggestion will strictly be catered to that. Solar emporium does not favour the non-renewable options of power generation for any off the grid property because of the extreme effects on the environment happening right now.
To power your off the grid home, you can choose the following power generation options (renewable)-
- Solar panel system
- Wind electricity
- Micro hydro electricity
Solar Panel System
There are many ways to be energy independent and have no carbon footprint, like using wind and water electricity, but the process is time consuming and needs ongoing maintenance. A residential off-grid house that uses a power source other than solar is therefore uncommon. Without much effort on your part, solar energy can give your house the constant electricity it needs to run and store some more.
Wondering how solar panels work? Solar panels function by reacting when sunlight strikes them. The amount of energy generated depends on the angle and intensity of the sunlight, but solar panels will continue to produce energy for as long as they receive sunlight. After that, a solar inverter transforms it into useable electricity, which you may use to power your house.

In an off grid home, you are required to have solar batteries tied to the system. This way, you can reserve the surplus of energy generated by your panels to use later. Also, a charge controller is essential, which can determine the flow of electricity either to the house or the battery, also control when to switch to the backup generator if required.
Kilowatts, or kW, are the unit of measurement for a solar system’s power rating. It is a measurement of the size of your solar system, not the amount of energy it will generate. The size of your system (x kW) is multiplied by the Peak Sun Hours unique to your area, which vary between summer and winter, to get the kWh (kilowatt hour). The generated energy, measured in kWh, will initially be used to power the house’s daytime loads before being used to charge the battery bank.
Solar panels are the ideal choice for your off grid home among the other power generation alternatives.
Here is why-
Advantages of Solar Power
- Easy installation process.
- Requires little to no maintenance and labour.
- Solar panel prices are dropping at an astonishing rate with recent technological advancements.
- Government rebate under the Renewable Energy Target (RET).
- A well-designed system can provide excellent ROI and pay for itself within a few years.
- No additional establishment is required to maintain the system.
- Sustainable and independent energy source.
- Fixing any issues, if faced, is extremely easy and can be done without any expert supervision in most cases.
- Does not require any additional connection fees or permissions.
Areas to Improve
- If solar panels could work at a 100% efficiency rate, the entire world could be powered by only 1 hour of peak sunlight hours. Which is a rather imaginative scenario but the system’s efficiency can always approach growth.
- With scientific revelations and effective supply chain management, the prices of a solar panel system have the potential to drop even more.
Wind Electricity
This is another option to generate power off the grid. It might not be the most feasible option if you do not have a lot of space in your off grid property. However, a 5 to 15 kW system is sufficient to provide for an average household’s monthly electricity needs. The efficiency rate of a wind electric system depends on the wind speed of the area, which can vary in different seasons.
A typical wind electric system which is enough to generate power for a single residential house can be at least 23-25 feet in diameter and 100 feet tall.
The rotor blades of a wind turbine, which function similarly to a helicopter rotor blade, convert wind energy into electricity using aerodynamic force. The air pressure on one side of the blade falls as the wind passes by. Both lift and tug are produced by the different air pressure on the blade’s either side. The rotor spins because the force of the lift is greater than the force of the tug.
If the generator is a direct drive turbine, the rotor is connected to it directly; otherwise, a gearbox that speeds up the rotation and permits a physically smaller generator is used. Electricity is produced as a result of the conversion of aerodynamic force into generator rotation.
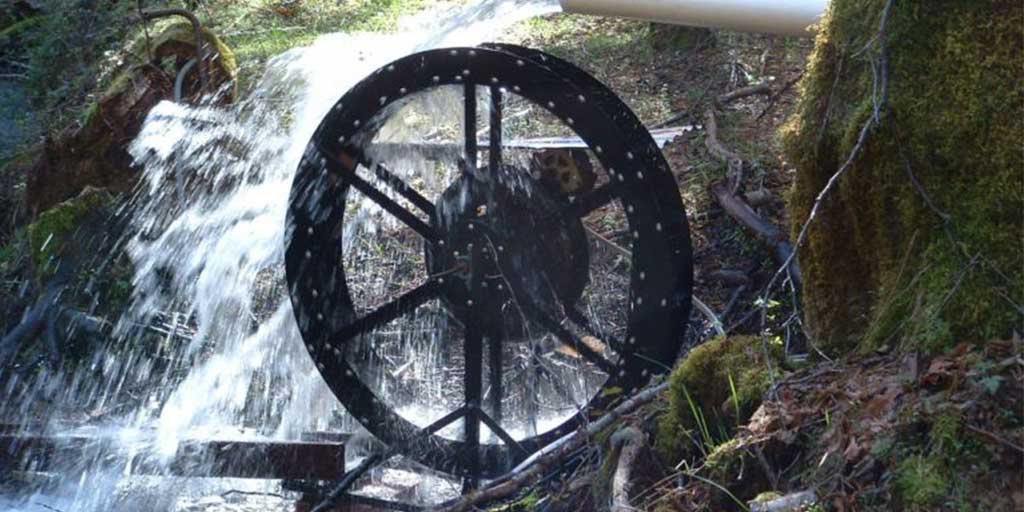

Micro Hydro Electricity
As the name suggests, the micro hydro electricity generation system requires water, a steady flow or stream of water. Using the kinetic force of a water stream micro hydro system can produce electricity to power any off the grid residential property. These off grid systems are usually the cheapest solution for any off grid home but with that comes some difficulties as well. It’s a high-maintenance system that requires quite a lot of attention.
Besides that, this is the most cost-efficient green energy source that can run 24/7 if designed properly. There are many commercial power plants that run on hydro electricity using a massive water stream, either man-made or natural, but a micro one is a miniature version of such systems.
The impact of the high-pressure water on these cups rotates an alternator, which produces energy. Batteries are typically charged by the alternator.
Maximum electrical output for hydroelectricity is determined by the formula: flow rate (litres per second) x head (meters) x 10. (watts). Therefore, a stream descending at 20 litres per second down a 10-meter head would have a 2000-watt maximum output.