Solar Power FAQs
Solar FAQs
The average solar panel system size is approximately 6.6 kilowatts (kW). However, the size can vary depending on the household’s energy consumption, roof space, and budget.
The average cost of a 6.6 kW solar panel system in Australia is $3,500 to $8,000. It depends on the quality of the panels and inverters, the complexity of the installation, and the location.
The average solar panel efficiency, which measures how much sunlight the panel can convert into usable electricity, is around 15-20% for most solar panels. However, high-end panels can reach efficiencies of over 22%.
Regarding energy production, Australia’s 6.6 kW solar panel system can produce an average of 24 to 36 kilowatt-hours (kWh) per day. This can cover the electricity needs of a medium to large household.
It’s also worth noting that Australia has one of the world’s highest solar panel installation rates, with over 2.4 million solar PV installations as of 2020. It is largely due to the country’s abundant sunshine and government incentives for solar power.
The best solar panel size for a household in Australia depends on several factors, including the household’s energy consumption, the size and orientation of the roof, and the budget.
However, Australia’s most common solar panel system size is 6.6 kW. This is because it is currently the maximum system size that can be installed to receive the full benefit of the government’s Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme.
A 6.6 kW system is typically sufficient for an average-sized household (3-4 people) with moderate electricity usage. It can generate an average of 24 to 36 kilowatt-hours (kWh) per day, which can cover most or all of the electricity needs of such a household.
A larger system may suit larger households or those with higher energy consumption. For example, if you have a pool or use air conditioning extensively, you need a bigger system.
It’s always best to consult a solar professional who can assess your needs and recommend the most suitable system size.
A residential solar panel size can vary depending on the specific model and manufacturer. Solar panels come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Some are more productive than others. A residential solar panel is typically 65 inches by 39 inches in size.
In other words, most solar panel is typically about 1.6 meters tall and 1 meter wide. It equates to a total area of about 1.6 square meters.
Each manufacturer’s product may differ slightly. But all manufacturers will specify the size of the solar panels.
In terms of capacity, the most common solar panel system size in Australia is 6.6 kilowatts (kW). It typically comprises around 20 individual panels. Each comes with a capacity of about 330 watts, depending on the specific panels used.
However, the number and size of the panels you would need for your home can vary depending on your energy usage, the size and orientation of your roof, and other factors. It’s always best to get a personalized quote from a solar provider.
There are several factors to consider when selecting solar panels for your home. Before you invest in a solar panel system, you must determine how much power you require. It will aid in determining the number of panels needed for your home. As a result, you’ll know how much weight you can expect to add to your home if you install a solar panel system.
Solar panels typically weigh around 40 pounds each. A professional installer like Solar Emporium can assist you in determining the overall weight of a solar panel on your roofing system.
While the size of the solar panels on your roof should be small, each panel’s quality and energy output should be. Here are some common advantages and disadvantages of larger solar panels:
Pros
- Reduces your electricity bills
- Produces more renewable energy
- Can add value to your home and future-proof any expanding energy needs
Cons
- Higher upfront costs than smaller systems
- Efficiency can still be impacted by weather or lack of sunlight
- Degrades over time
The Australian government offers several incentives and rebates to encourage the use of solar energy. These include:
- Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES): This scheme provides a financial incentive for individuals and small businesses to install eligible small-scale renewable energy systems such as solar panel systems, small-scale wind systems, small-scale hydro systems, solar water heaters, and air source heat pumps. It does this by creating small-scale technology certificates (STCs), which can be sold to recoup a portion of the cost of purchasing and installing the system.
- Feed-in Tariffs (FiTs): These are rates paid for excess electricity that your solar panels feed back into the grid. The rates vary by state and by energy retailer.
- Solar Battery Rebates: Some states offer rebates for installing solar batteries. For example, the South Australian Home Battery Scheme provides subsidies for installing home battery systems.
- Various State-Based Incentives: Different states and territories may have additional incentives or rebates. For example, Victoria has a Solar Homes program that provides a rebate for solar panel (PV) system installation, a rebate for installing a solar hot water system, and a rebate for installing a solar battery.
Read more about state-based incentives in our blog Best Solar Rebate And Incentive Guide for Australia.
These incentives and rebates can change. And it’s important to check the most current information from the Australian government and your state or territory’s government. As for 2023, you need to check closer to the time to see what incentives and rebates are available.
Yes. Small-scale Technology Certificates, or STCs, are available for all installations under 100kW (and systems with an annual electricity output of less than 250MWh). STCs are available whether you have previously used a rebate.
It is also not means-tested and is open to all. To qualify for STCs, the solar PV system or product you purchase must follow the Clean Energy Council (CEC) design and installation guidelines. You must use panels, batteries, and inverters from the CEC-approved list. These comply with relevant standards and be installed by a CEC-accredited installer.
The main solar rebate in Australia is the Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES), which provides small-scale technology certificates (STCs) for eligible solar installations. Here’s a simplified way to calculate the rebate:
- Determine the System Size: The number of STCs you can create depends on the size of your solar system (in kilowatts), the location of the installation, and the amount of electricity it’s deemed to generate or displace.
- Calculate the Deeming Period: The deeming period is the number of years until the end of 2030, which is when the SRES is set to end. For example, if you installed your system in 2022, the deeming period would be eight years.
- Use the STC Calculator: The Clean Energy Regulator provides an STC calculator on its website. You can input your system size, installation date, and location to determine how many STCs your system could generate.
- Determine the STC Price: STCs are traded in an open market, and prices fluctuate depending on supply and demand. As of 2021, the price is generally around $35 to $40, but you can check the current price online.
- Calculate the Rebate: Multiply the number of STCs your system could generate by the current STC price to estimate your rebate.
It’s also important to note that other incentives, like feed-in tariffs or state-based rebates, will have their calculation methods. Always consult with a solar professional or your energy provider for accurate figures.
Yes, it is worth installing solar panels in Australian households for several reasons:
- High Solar Potential: Australia has one of the highest solar potentials in the world, with most parts of the country receiving more than 4 kWh per square meter per day of solar energy.
- Government Incentives: The Australian government offers incentives for solar panel installation, such as the Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme, which provides certificates that can be sold to recoup some installation costs.
- Lower Energy Bills: Solar panels can significantly reduce electricity bills. Any excess electricity generated can be fed back into the grid, and you may receive a credit on your bill.
- Environmentally Friendly: Solar energy is a clean, renewable source of energy that can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Increase Property Value: Homes with solar panels tend to have higher property values and sell more quickly than those without.
- Energy Independence: By generating your electricity, you are less dependent on the grid and less affected by electricity price increases.
However, installing solar panels can be expensive, and it may take several years to recoup the investment through energy savings. It’s also important to note that solar panels are most effective on roofs with good sun exposure, so they may only be suitable for some properties.
Solar panels will be a good investment in every Australian state, regardless of electricity consumption, in 2023.
While many factors influence solar panels’ cost, savings, and payback, the bottom line is that they are a good investment in Australia. Solar panel systems typically pay for themselves in 5 – 6 years, and it is not uncommon for systems to pay for themselves in 4 years.
If you buy wisely, a good solar power system should save you money for 25 years.
Solar energy is relatively cheap in Australia compared to many other countries. It is possible due to a combination of factors, including the country’s abundant sunshine, government incentives, and the falling cost of solar technology.
As of 2021, the average cost of a standard 5kW solar system in Australia ranges from AUD $3500 to $6000 after government rebates have been applied. The price is significantly lower than a decade ago.
Moreover, the cost of solar power is expected to continue decreasing. Combined with rising electricity prices, it makes solar an increasingly cost-effective option for many Australian households.
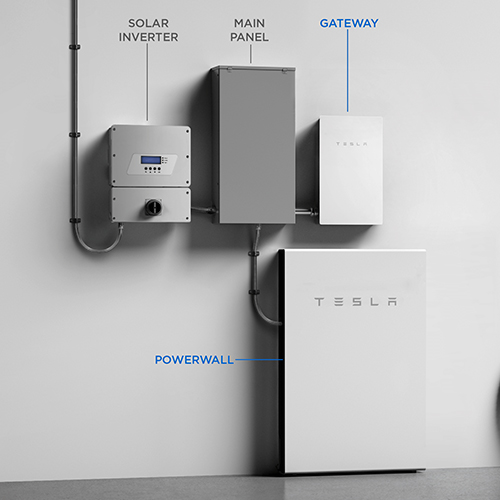
Solar battery storage is a system that stores excess solar energy produced by your solar panels for later use. During the day, your solar panels may produce more electricity than your home needs. It can be stored in a solar battery instead of returning this excess power to the grid.
Then, at night or on cloudy days when your solar panels aren’t producing as much electricity, you can draw on the energy stored in your solar battery instead of drawing power from the grid. It can reduce your electricity bills and increase your home’s energy independence.
It’s critical to note that while solar batteries can increase the efficiency of a solar power system, they also add a significant cost to the system, and it may take many years to recoup this cost through energy savings.
Solar plus storage refers to a solar power system that includes solar panels and battery storage.
Solar panels generate electricity during the day, which can be used immediately to power your home. If the panels produce more electricity than your home needs, the excess power is stored in the battery instead of being returned to the grid.
Then, when your solar panels aren’t producing electricity (like at night or on cloudy days), you can use the power stored in the battery. It allows you to use solar power even when the sun isn’t shining, making your home more energy-independent and reducing electricity bills even further.
Solar plus storage systems can also provide backup power in case of a power outage, depending on the system setup.
- SunPower offers some of the most efficient solar panels. They also have a strong warranty and a wide range of panel options.
- Q CELLS is a popular choice in Australia due to its high efficiency, reliability, and value for money.
- Trina Solar is one of the world’s largest solar manufacturers of panels and is known for its high-quality, durable panel.
- Jinko Solar is a global leader in the solar industry. Their panels are highly efficient and reliable.
- Canadian Solar is one of the’s world largest solar energy companies and a leading manufacturer of solar photovoltaic modules.
- REC is a leading global provider of solar energy solutions. Their panels are known for their high quality and efficiency.
- LONGi Solar is a world-leading manufacturer of high-efficiency mono-crystalline solar cells and modules.
- Seraphim specializes in the research, development, production, and sales of solar PV products.
- Risen Energy is a leading, tier global manufacturer of high-performance solar photovoltaic products.
Selecting a specific solar brand entirely depends on you and your particular situation. You must consider your financial state, residence, living area, energy consumption, and overall condition. There are other important factors involved too. Like which installer company you are picking or where to mount your panels.
You can check out our solar packages and talk to a solar expert for a better understanding.
Various factors, including the orientation of your roof, the angle of the panels, the weather, the seasons, and the size of your system, determine this. As a result, we only use averages and guidelines from the Clean Energy Council.
To simplify things, a 2kW system should produce 7.8kWh per day, while a 10kW system should make 39kWh per day. Using this figure, a simple yet effective way to estimate the output of an installed solar system is to multiply the system size by 4 (or 3.9 in this case). An average day, a 2kW system will generate approximately 7.8kW/h of power.
STCs are acronyms for Small-scale Technology Certificates. These tradeable certificates are created when you install a small-scale renewable energy system, such as solar power, solar hot water, or heat pumps. These STCs fluctuate in value but are currently worth about $35 each, which equates to about $3,750 on a 6.5kW system in most areas. Almost all solar companies will quote you a price that includes the discount, which means you only have to pay the difference after these reductions are applied.
The number of STCs for hot water and heat pumps are best determined by going to the REC registry website and entering the system details, as they keep the most up-to-date catalogue of information.