In recent years, solar energy has become an important renewable energy source in Australia. The country gets some of the highest sunlight worldwide, making it a great place to use this natural resource.
In this article, we will look at the challenges and opportunities in Australia’s solar industry, how the industry is doing now, and what the future might hold for solar energy in the country.
Australia is sunny most of the year, providing a great chance for solar energy. With lots of land that gets direct sunlight, the country is in a good position to lead the world in renewable energy.
This potential calls for a smart approach, combining new ideas with government support, to create a future where solar energy is a key part of Australia’s renewable energy system.
Energy Sources in Australia
Australia mostly uses fossil fuels like coal and natural gas for its energy. These sources have been important for many years but have some downsides.
Coal: Coal has been Australia’s main energy source, powering industries, homes, and the economy.
However, coal is a limited resource and harms the environment. Mining and burning coal cause air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and habitat damage. Australia is slowly closing coal power plants and seeking cleaner energy options to address these issues.
Natural Gas: Natural gas is cleaner than coal and is seen as a temporary solution, but it is still a fossil fuel with a limited supply. Relying on natural gas poses sustainability challenges. Australia aims to balance natural gas use with renewable energy to lower its carbon footprint.
Renewable Energy: Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power are becoming more popular. These sources are better for the environment and more sustainable.
Australia has plenty of sunlight and wind, making it ideal for renewable energy. Investments in solar and wind farms and hydroelectric projects are changing the energy landscape.
Current Energy Demand
Different sectors in Australia use energy in various ways.
Residential Consumption:
Homes use a lot of energy for appliances, heating, cooling, and lighting. More homeowners are choosing energy-efficient appliances, LED lights, and better insulation to reduce energy use.
Industrial Consumption:
Industries like manufacturing and mining use a lot of energy to run. They are looking for energy-efficient technologies and switching to cleaner energy sources to lessen their environmental impact.
Commercial Consumption:
Offices, shopping centers, and other commercial buildings also use much energy. Businesses use energy management systems and design sustainable buildings to reduce energy use and costs.
Opportunities in Australia's Solar Industry
Abundant Solar Resources
Australia is a great place for solar energy because of its natural advantages.
Australia receives some of the most sunlight globally. This means a lot of solar energy is available, making it a perfect environment for producing solar power. Solar panels can easily capture strong sunlight to generate electricity efficiently.
Australia has large areas of land that are not heavily populated. These wide-open spaces are perfect for setting up solar farms, which are large solar panels that produce a lot of energy.
Because these areas don’t have many people, there is less chance of conflicts over land use. Solar farms can be built without removing space from homes or other important uses.
This setup generates much clean energy, making the most of the available land and sunlight.
Technological Advancements
Australia is also benefiting from new technologies that make solar energy even better.
Improved Efficiency: Solar panels are getting better at converting sunlight into electricity. This means they can produce more power with the same amount of sunlight.
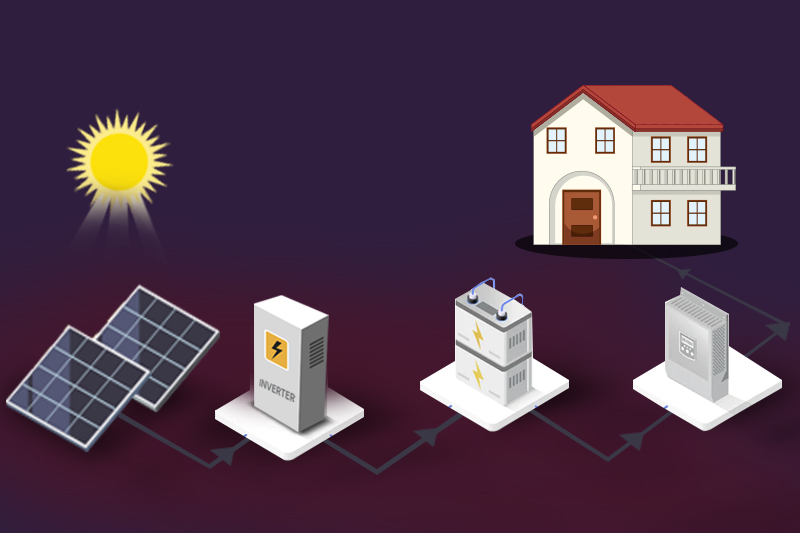
Advances in battery storage technology also allow us to store the energy generated by solar panels more efficiently. These improvements help lower the overall cost of solar power, making it more affordable and practical for everyone.
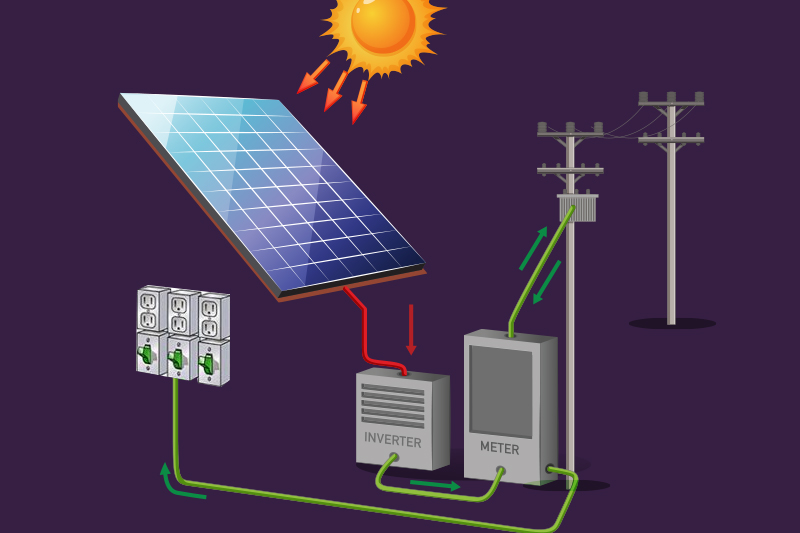
Smart Grids: Smart grids are advanced systems that help manage the electricity supply more effectively. They can automatically balance the amount of energy produced and used, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply.
Using smart grids, Australia can more smoothly integrate solar power into the existing electricity network. This helps prevent power outages and makes using solar energy alongside other energy sources easier.
Decentralized Energy Systems
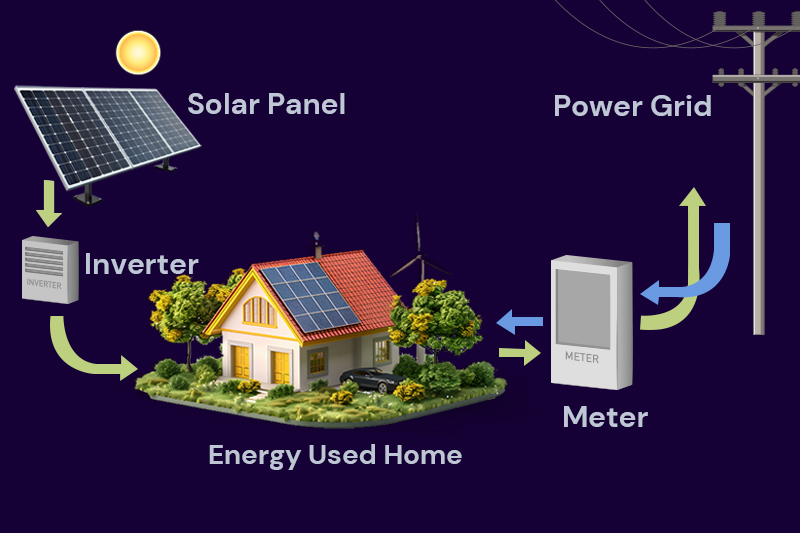
Rooftop Solar: Many homes in Australia have solar panels on their roofs. This is called rooftop solar. This makes the energy system more efficient and enhances energy security because people can produce power.
Microgrids: Microgrids are small, local energy networks that can operate independently or alongside the main power grid. These are especially useful in remote and rural areas where connecting to the central power grid can be difficult and expensive.
Microgrids can use local renewable energy sources like solar power to provide reliable electricity to these areas. This reduces the reliance on large, centralized power systems and helps ensure that even remote communities can access stable and consistent power.
Economic Growth and Job Creation
The solar energy industry in Australia can greatly boost the economy and provide many job opportunities.
Employment: The solar industry can create many types of jobs. People will be needed to manufacture solar panels, install them on rooftops and solar farms, and maintain the equipment to ensure it works properly.
Investment: Solar energy can attract money from both inside and outside Australia. When businesses and governments invest in solar projects, it can lead to economic growth.
This investment helps develop new technologies and create more efficient solar power systems. As more money is put into the solar industry, it can encourage other sectors to innovate and grow, leading to a stronger overall economy.
Government Support

The government plays a crucial role in supporting the growth of solar energy in Australia. Here’s how they help:
The government offers various incentives to encourage people and businesses to adopt solar energy. For example, they provide rebates, which are partial refunds, to help cover the cost of installing solar panels.
This makes it more affordable for people to switch to solar power. Additionally, the government funds research to develop better solar technologies, which can lead to further improvements and cost reductions in the future.
The government sets clear goals for how much of the country’s energy should come from renewable sources like solar power.
These renewable energy targets give the industry a clear direction and help ensure everyone is working towards the same goal.
Long-term targets also provide stability, meaning businesses and investors can confidently plan for the future, knowing there is strong support for renewable energy.
Challenges in Australia's Solar Industry
Initial Installation Cost
Solar and wind energy are the cheapest sources of energy overall. However, the upfront costs of installing a solar power system are much higher than those of a gas-fired plant.
Installing a large-scale solar power system costs about $2,000 per kilowatt, while a small home solar system costs around $3,700 per kilowatt.
In contrast, building a new gas-fired plant costs about $1,000 per kilowatt. The big difference in installation costs is clear.
Because of these high initial costs, investors and lenders see renewable energy as a higher risk, while they find fossil fuels more appealing due to their lower installation costs.
Energy Storage
One of the most frequently discussed issues is efficient, cost-effective, and reliable energy storage. Developing a better storage system has historically been one of the most challenging aspects of renewable energy generation.
Because of variations in sunlight and wind, supplies are less reliable than those derived from fossil fuels. As a result, owners rely on batteries to store energy for future use. And to even out energy supply disparities.
Concerns have been raised about the cost of this technology. That also raises the issue of sustainability.
Monopoly of the Non-renewable Energy Industry
The non-renewable energy industry has a strong grip on the energy market, making it hard for renewable sources like solar and wind power to compete. The government subsidizes solar energy, but fossil fuels get even more support.
Renewable energy is the best way to fight climate change. However, fossil fuels have been a big part of our economy for a long time and are deeply rooted in it.
Future of Solar Energy in Australia’s Landscape
The future of solar energy in Australia looks promising because the country gets a lot of sunlight throughout the year.
Australia’s vast land areas receive direct sunlight, making it a perfect place to lead the global shift to renewable energy. However, the full potential of solar power in Australia is starting to be understood.
It’s about more than just putting up more solar panels to harness Australia’s solar power potential fully.
It involves rethinking how we use and sustainably make energy. Australia’s strong sunlight means that using even a small amount of land for solar farms could make a big difference in powering the country.
To make this happen, we need smart planning that combines new ideas with government policies to create a future where solar energy is a major part of Australia’s energy supply.
Solar Emporium is active 24/7 to serve your solar energy needs. Contact Solar Emporium or get a free solar quote today!