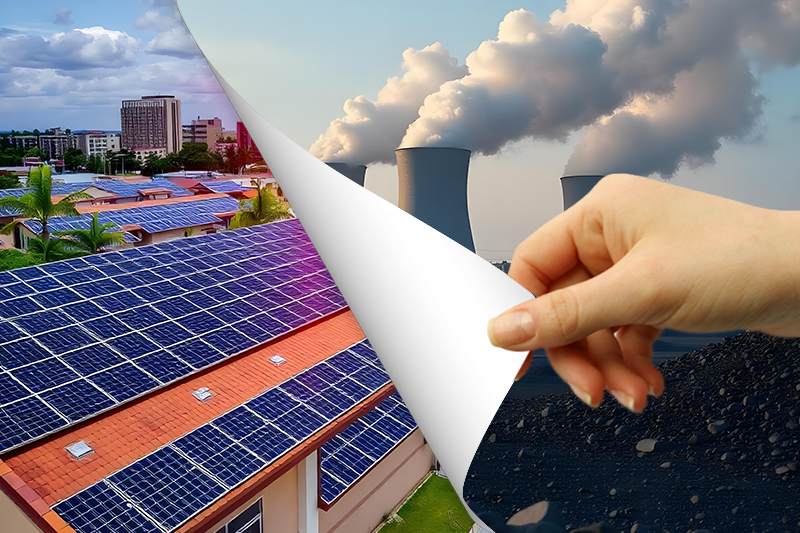
As the planet’s temperature rises, ecosystems are heavily strained under extreme weather events and natural disasters. But what if we could reduce environmental pollution simply by making polluters pay for the damage?
Yes, the carbon tax just aims to do that!
When the world is fighting against climate change and suffering badly from the detrimental effects of global warming, carbon taxation emerged as a potential solution.
By imposing a tax on carbon emissions and making carbon-intensive activities more expensive, this approach significantly helps reduce our carbon footprint. So, how does carbon tax help fight climate change? How carbon pricing work?
In this blog, we’ll explore these questions to determine whether Australia should reintroduce or reconsider carbon taxation as part of its climate policy.
So, without any further ado, let’s get started!
Carbon Emission: The Silent Driver of Climate Chaos
In Australia, Fossil fuels, such as coal, gas, and crude oil, account for 91% of the country’s primary energy mix. And that’s where the problem lies!
Burning fossil fuels to generate energy is one of the primary sources of carbon emissions and a leading driver of climate change.
Human activities such as heating, cooking, and transportation burn nonrenewable energy sources, releasing ample amounts of carbon into the atmosphere.
The emission of greenhouse gases (GHGs) usually traps the sun’s heat, creating a greenhouse effect. It raises the global temperature bringing some deadly consequences to the environment, such as melting glaciers, rising sea levels, and disrupting weather patterns.
Also, due to industrialization, deforestation, and insufficient adoption of renewable energy sources in Australia, carbon emissions have escalated further in the past few years.
According to available data, temperatures are assumed to rise by about 4°C above pre-industrial levels by the end of the century if no serious measures are taken.
So, don’t you think the urgency of reducing carbon emissions has never been more critical before for ensuring a livable planet for future generations? Certainly, yes!
What is a Carbon Tax?

A carbon tax is a policy that imposes a financial charge on fuel’s carbon content. By increasing the price of carbon, the policy aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning more towards a bright, sustainable future.
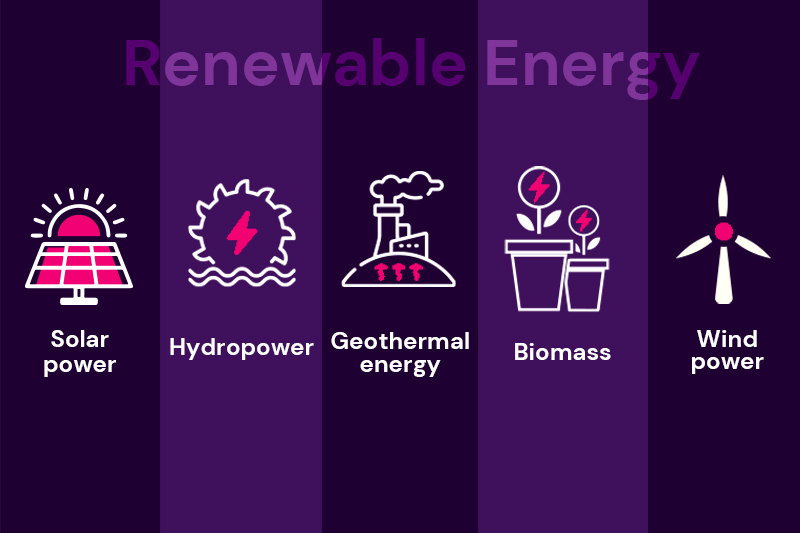
The carbon tax makes high-emission energy sources more expensive, prompting businesses and homeowners to seek alternative clean energy options, such as wind, solar, and other renewable energy sources.
The carbon tax has a complex history in Australia. In 2012, the Gillard government introduced it by setting a fixed price based on the users’ per-ton CO2 emissions.
Unfortunately, the carbon tax policy wasn’t a success for Australians and turned out to be less effective. Residents felt that the tax raised electricity prices, and political parties argued that it harmed their economy without significantly reducing emissions.
So, in 2014, the Abbott government abolished the carbon tax and focused on other practical approaches, such as introducing policies for solar energy adoption and building the Emissions Reduction Fund (ERF), as well as renewable energy targets to cut emissions.
Turning Taxes into Climate Action: How Carbon Pricing Works to Reduce Emissions?

Even though a carbon tax is a costly solution, it is one of the best policies for adopting cleaner technologies and transitioning to sustainable energy sources.
It encourages energy efficiency, reduces our carbon footprint, and reduces our heavy reliance on fossil fuels.
Moreover, the revenue generated by carbon taxation can be invested in sustainable energy projects and energy efficiency programs. In some Australian states, these revenues can also offset the tax burden on lower-income households.
Altogether, carbon taxes help accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy while generating funds that can be reinvested in sustainability efforts.
So, here’s how carbon tax works:
- Initially, the government set a tax on fossil fuels; for example, the amount could be 10 AUD per ton of CO₂. So, emitters must pay for each ton of greenhouse emissions they contribute to the atmosphere.
- Different fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) have different carbon contents, so the calculation also varies. For instance, burning one ton of coal produces more CO₂ than burning one ton of natural gas, so the tax on coal would be higher.
- The carbon tax increases the production and transportation costs of goods that rely heavily on fossil fuels. Ultimately, this increases the prices of many products and services that involve carbon-intensive processes.
- Carbon taxation encourages behavioral change in consumers influencing them to embrace more energy-efficient, lower-emission alternatives.
Examples include electric vehicles for transportation, solar panels for electricity generation, and using heat pumps instead of oil and gas heaters.
- Through carbon taxes, people can participate in revenue recycling, where the government returns a portion of the carbon tax revenue to consumers and businesses.
This revenue reduces personal income taxes, effectively recycling the funds into the economy.In some places, the tax revenue is directly given back to citizens as cash rebates.
Australia's Carbon Tax: Is It Back in 2024?
One of the burning questions people often ask is whether Australia is reconsidering its approach to carbon taxes. If not, what will replace It in 2024?
Well, the country has committed to reaching net-zero emissions by 2050 and has introduced other empowering home programs, climate policies, incentives, and emissions reduction targets.
Though there is no formal carbon tax in Australia, the other market-based mechanisms are effective in combating climate change.
The government’s stance is still evolving, and the political and social collaborative effort on sustainable practices shows a promising future where every home in Australia is powered by clean, renewable sources.
How Does a Carbon Tax Help Fight Climate Change?
If done right, carbon tax helps fight climate change by reducing GHG emissions, changing household and consumer behavior, and driving the development and adoption of technologies.
With the higher carbon prices, this policy drives deeper emissions reductions. It plays a key role in building a low-carbon economy while shifting us away from fossil fuels, changing our emissions trajectory.
Also, don’t forget about all the monetary benefits the tax brings. It helps by ensuring financial aid and minimizes the initial cost barrier to sustainable energy transition for low-income households.
In the upshot, carbon tax encourages individuals, businesses, and governments to reduce Australia’s dependency on fossil fuels.
It ensures residents invest in cleaner alternatives and take a more proactive role in mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Why a Carbon Tax Could Be Australia's Key to Fight Climate Change?

Australia is one of the largest per capita emitters of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the world.
The alarming part is the country’s per capita emissions are much higher than the global average.
Accounting for 14.3% of total global reserves, the country is known for having the third-largest coal reserves in the world.
Similarly, Australia’s vast coal mines and abundant reserves make it the fifth-largest producer and the second-largest coal exporter worldwide. Burning fossil fuels, particularly coal, is one of the biggest contributors to global warming.
However, still in 2024, coal is the main source of reasonably priced, dependable electricity for the Australian economy. Around 62.6 percent of the electricity sold in the National Electricity Market came from coal.
So, now it’s clear that the country’s high dependency on fossil fuels is what makes it challenging to achieve a 100% renewable transition within a short time frame.
Therefore, reintroducing the carbon tax along with other government policies can speed up the energy transition process in Australia. Together, they can reduce emissions, address growing environmental concerns, fight climate change, and provide various incentives.
Overall, carbon taxation can create a comprehensive strategy that supports a smoother and faster transition towards a sustainable energy future for Australians.
The Carbon Tax Dilemma: Environmental Solution or Economic Burden?
After all, the question of whether a carbon tax is the right tool to tackle climate change remains unsolved.
Still, there is considerable debate over whether a carbon tax is effective in combating climate change. While many economists and climate advocates support the carbon tax, there are also people who feel this is an additional financial burden.
So, here are the pros and cons of a carbon tax in Australia’s energy landscapes:
Advantages of Carbon Tax in Australia
- Adding a carbon tax reduces carbon emissions and pollution. It makes polluters pay for the emissions they create, making them more sincere about environmental health.
- Generates government revenue that can be used for sustainable environmental projects, educational training, and rural energy development programs.
- Taxation on carbon emissions promotes innovation. It encourages businesses to invest in cleaner technologies and sustainable practices, switching to renewable energy sources.
- A carbon tax is relatively simple and straightforward to implement compared to more complex regulatory frameworks. This makes it easier for businesses and governments to understand and adjust to it.
Disadvantages and Challenges of Carbon Tax in Australia
- Increased operational costs for industries reliant on fossil fuels could potentially lead to job losses and business closures. It would also increase the prices of goods and services, especially energy and transportation.
- It affects people with lower incomes who are dependent on the fossil fuel industry, raising equity concerns in Australia.
- Australian markets may face a competitive disadvantage in global markets if other countries do not implement similar carbon pricing mechanisms.
- Effective monitoring and enforcement of carbon tax can be difficult.
- While it provides an economic incentive to reduce emissions, the tax alone may not be sufficient to achieve significant reductions in greenhouse gases without complementary policies.
- A carbon tax can impact people in rural, remote areas or regions that rely heavily on energy-intensive industries such as mining, agriculture, etc.
Parting Thoughts
While many people agree that carbon tax could accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy and help fight climate change, critics argue that it may place an unnecessary economic burden on households and businesses.
However, everything in the universe comes with positivity and negativity. So, once you replace the negative side of carbon taxation with positive ones, you’ll start having good results.
Contact Solar Emporium today to learn more about renewable energy and receive updates about renewable energy in Australia!
Here, we also offer exciting solar packages to make your energy transition process much smoother and more efficient.