Australia is on the verge of a groundbreaking transformation in its energy sector, boldly stepping into the future of renewable energy.
With the country’s ambitious plans and significant investments lined up for 2024-25, Australia is already a global leader in the clean energy sector.
However, as Australia moves forward with its sustainable energy goals, its focus has become more coherent and intense over the years. Also, the government, private sector, residents’ collaboration, and strong commitment have further accelerated the shift.
But how strong is the level of support for Australia’s renewable sector? Wondering what’s driving this shift?
Don’t stress over it! In this blog, we’ll explore the factors fueling Australia’s renewable energy revolution and what its future holds.
So, let’s take a closer look at key statistics, government initiatives, and the role of technology in helping the nation meet its renewable energy targets!
The Rise of Renewables: Major Energy Projects in Australia
Over the past decade, Australia has seen significant progress toward renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, hydroelectric, and, most importantly, innovative battery technology, which helps to mitigate the challenges of renewable energy storage.
As of 2024, renewables contribute approximately 32% of Australia’s total electricity generation, with solar and wind accounting for the largest shares.
With an ambitious target to achieve 50% renewable energy by 2025 and a long-term goal to decarbonize its economy, Australia is moving fast toward a greener, more sustainable energy future.
Solar Power
- Australia is geographically blessed with vast sunlight resources, which makes solar power a key player in the country’s renewable energy strategy.
The government incentives, falling battery costs, and the public’s high solar energy adoption rates have driven significant growth in solar installations.With millions of homes harnessing solar energy daily, Australia now ranks among the world leaders in residential solar power.
Wind Power
- Wind is another renewable source that has gained traction recently, particularly in regions with heavy and suitable wind conditions. Wind power generates electricity using wind turbines that capture kinetic energy from moving air.
Several onshore and offshore wind farms in Australia are operating efficiently to provide a clean energy supply to the country’s residents.
Hydro Power
- If you live near a water body, hydropower can be your reliable partner on days with frequent power outages due to grid failure. Why? Hydropower generates electricity by deriving the energy from flowing or falling water.
Large- and small-scale projects, such as the pumped storage hydro systems available in Tasmania or Snowy Mountain, can significantly generate huge amounts of electricity and provide long backup power. Overall, they contribute to Australia’s renewable energy goals while providing a stable power source.
Battery Storage and Grid Modernization
- Battery Storage Renewable energy, such as solar and wind, is intermittent. As it is not always available, 6kWh or 10-kWh battery storage systems can be crucial for storing excess energy during peak times. Batteries improve the reliability and stability of renewable energy integration, ensuring energy security for all.
- Grid Modernization Modernized grids offer improved efficiency and reliability. They include innovative smart grid technologies, better communication systems, and improved energy storage capabilities to match supply with demand better. For example, solar batteries integrated with smart grids increase efficiency, allow grid stability, and save costs by reducing electricity bills.
- Hornsdale Wind Farm Location: South Australia capacity: 315 megawatts (422,000 hp) It is one of the largest wind farms in South Australia, consisting of hundreds of wind turbines that generate renewable energy. This farm is contracted to supply the generated electricity to the Australian Capital Territory.
- Bungala Solar Project Location: South Australia capacity: 275 MW The Southern Hemisphere Bungala Solar Project, with a capacity of 275 MW, is known as the largest solar project. It helps to minimize the carbon footprint and reduce Australia’s high dependency on fossil fuels, particularly coal.
- Macarthur Wind Farm Location: Victoria, Australia Capacity: 420 MW This wind farm consists of 140 turbines, producing enough electricity to power 220,000 homes. It can reduce 1.7 million tons of greenhouse gas emissions yearly.
- Tesla Hornsdale Power Reserve Location: South Australia Capacity: 150 MW/194 MWh Tesla built Hornsdale Power Reserve in 2017, with the world’s largest lithium-ion battery storage facility. It was further expanded in 2020 to 194 MWh to support the grid, provide backup power, and reduce energy costs in South Australia.
- Ararat Wind Farm Location: Northeast of Ararat in Victoria Capacity: 240 MW With 75 turbines, the Ararat wind farm contributes significantly to increased wind energy capacity and helps Victoria meet its renewable energy targets.
- Yandin Wind Farm Location: North of Perth, Yandin, Australia Capacity: 214 MW Constructed in late October 2020, the Yandin wind farm comprises 51 turbines with 105 meters or 344 ft hub heights to maximize performance depending on specific wind conditions. It was designed to provide a clean, reliable energy alternative in Western Australia.
In addition to the abovementioned project, many renewable projects, such as the Australian Renewable Energy Hub, Kidston Renewable Energy Hub (Queensland), and Snowy 2.0, are still in the early or under-development stage.
However, the main goals of these projects are not only reducing global carbon dioxide emissions but also securing energy independence while boosting the economy through job creation and technological advancements.

Australia Aims for 50% Renewable Energy by 2025
Australia has set a bold target of achieving 50% renewable energy by 2025 and 82% by 2030, ultimately reaching net-zero emissions by 2050.
This ambitious goal represents the country’s commitment to combating climate change and the economic opportunities that come with these clean, sustainable, renewable energy sources.
The next few years will be critical in determining whether the country can reach this milestone and set itself on track to achieve its renewable goals.
Achieving this target will require continued investments in renewable energy infrastructure, such as solar farms, wind farms, energy storage systems, and electrification in the transport sector.
Growing Awareness of Climate Change
For the past few years, Australia has been feeling the detrimental effects of climate change.
The frequent bushfires, extreme cold and intense heat waves, floods, and droughts indicate it is high time to combat climate change and look forward to a sustainable energy transition.
However, government and private sectors are already supporting and investing heavily in renewables for the country’s environmental sustainability and betterment.
Cost Savings, Economic Growth, and Energy Independence
Who can resist the opportunity to lower energy bills and take control of their future by doing something good for the planet? None!
Renewable energy is not just about combating climate change; it’s also an economic driver for Australia.
Investing in renewables helps to reduce Australia’s reliance on imported fossil fuels, enhancing energy independence. The growth of the renewable energy sector also creates thousands of jobs, fosters innovation, and drives regional economic growth.
Government Support and Policies on Renewables
The Australian government has been supporting the renewable energy transition through various policies and programs. They also run educational campaigns, renewable projects, and energy efficiency programs.
At the federal level, the Renewable Energy Target (RET) requires energy retailers to source a portion of their energy from renewable sources.
The government has also introduced several funding programs to encourage investments in clean energy technology, including incentives for solar batteries and various schemes for low-income households to make renewable energy widely accessible.
In addition to federal policies, individual states and territories have developed their renewable energy targets.
How Public and Government Support Fuels Australia’s Renewable Energy Goals?
Public and government support is crucial to the success of Australia’s renewable energy transition.
Over the past decade, Australians have become extremely supportive of renewable energy. With government policies, several renewable targets, and sustainable practices, this level of support has become stronger than ever.
According to the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA), 85% of Australians currently support the transition to renewable energy, with a clear preference for solar and wind as the dominant, reliable, and clean power sources.
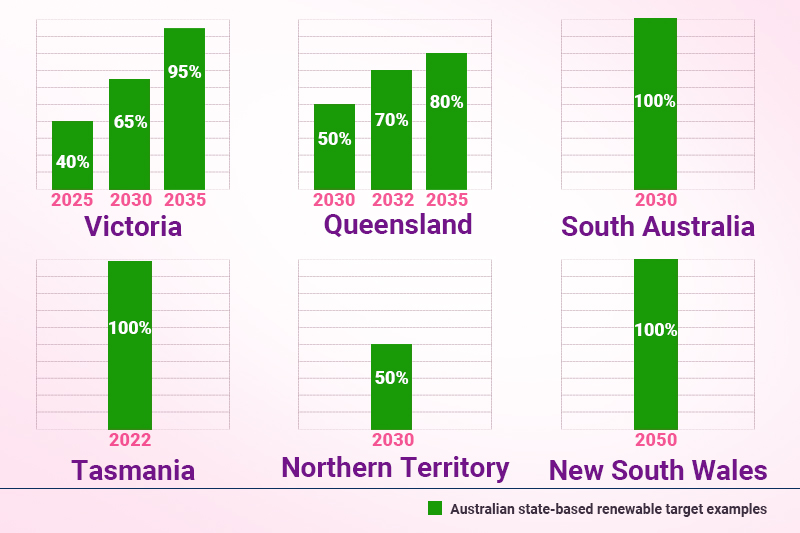
Australia’s Renewable Energy Targets: Comparing State-Specific Goals and Achievements in 2025
We know that Australia’s renewable energy targets are ambitious by now, but did you know they vary across states and territories?
Each state’s achievements and goals depend on its unique resources, infrastructure, and government policy frameworks.
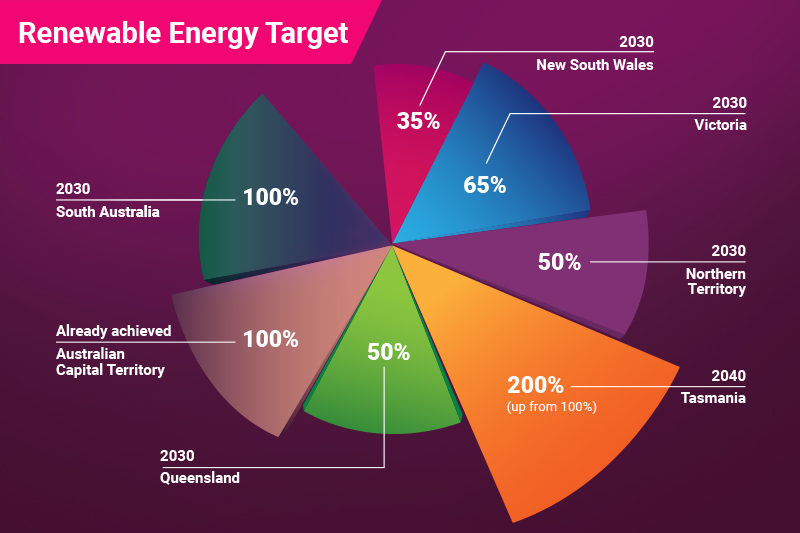
For example, in 2025, Victoria is expected to achieve 50% renewable energy, while New South Wales is targeting 35% by 2030. In the meantime, South Australia has already achieved its goal of 50% renewables and is on track to reach 100% by 2030.
| Australian State and Territory | Renewable Energy Target |
|---|---|
| New South Wales | New South Wales aims to reach 35% renewable by 2030 and increase its electricity generation capacity in the coming years. |
| Victoria | Initially, the state focused on reaching 50% renewables by 2030, but later, in 2023, they announced and legislated an increase of up to 65%. |
| Northern Territory | According to the Northern Territory government, the state aims to generate 50% of electricity from renewable sources by 2030. |
| Tasmania | Blessed with natural resources, Tasmania already reached its 100% renewable electricity target in 2022. The state is working to reach its new goal of 200% renewables by 2040. |
| Queensland | Queensland is focusing on solar power, with large-scale projects and a growing battery storage market to reach its 50% renewable energy target by 2030. |
| Australian Capital Territory | Like Tasmania, The ACT also reached its target early, sourcing 100% of its electricity from renewable sources like wind and solar. |
| South Australia | South Australia is already a leader, generating 50% of its electricity from wind and solar. The state is still working efficiently to reach 100% renewables by 2030. |
The Path Forward for Australia’s Renewable Energy Sector
Looking to the future, Australia’s renewable energy sector faces both opportunities and challenges. Key areas for development include expanding energy storage capacity, upgrading the electricity grid, and increasing investment in green hydrogen and bioenergy.
Ongoing renewable energy innovations, such as new materials for solar panels, offshore floating wind farms, and technological advancement, can enhance overall energy efficiency.
Moreover, international cooperation and partnerships with neighboring countries will be essential to ensuring Australia remains a global leader in renewable energy.
Australia’s Bright Renewable Energy Future: Is 100% Renewable Transition Possible?
In 2025, Australia’s renewable energy sector already started to thrive, with strong public support and an increasing share of the nation’s electricity generation from renewable sources.
Along with a clear vision, Australia has focused on a bright future powered by renewable energy. Even while the challenges remain regarding grid stability and energy storage, the path to a future 100% renewable energy transition is well within reach.
The country can achieve a fully decarbonized energy sector with the right policies, investments, and technological innovations.
The year 2025 is just the beginning! With the support of Australians, investment in renewables, and continued advancements in clean energy technology, Australia is on track to build a more sustainable, energy-independent future.
Want to power your homes with a clean, green, and abundant renewable energy source?
Contact Solar Emporium today and check out our best deals on solar packages!